The five benefits of federated data analysis

Hannah Gaimster, PhD
Introduction
In research and healthcare, the size of datasets needed to solve crucial problems is continuing to increase. New technologies including the digitisation of healthcare tools, the accumulation of electronic healthcare records and massively reduced costs for high throughput technologies like genome sequencing all contribute to these large datasets.
However, secure storage and analysis of these large, sensitive datasets is becoming significantly harder. There are three key reasons for this:
- Globally, there are increasing restrictions on data access to help keep sensitive information private (eg. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR))
- These datasets are large and can be hard to manage, making it difficult for researchers to identify the right data for their analyses.
- Datasets reside in disparate labs and clinics in locations across the globe. Because of this, they are all too commonly effectively siloed as strict data governance laws do not allow the data to be moved and copied.
Data federation is solving the problem of data access, without compromising data security
Researchers and clinicians are missing out on the potential that these huge health datasets can bring as they are difficult to access and combine for analysis for risk of compromising security. Research progress and patient benefits are stalling due to inefficient models for secure health data access.
Data federation as a solution
Data federation is solving the problem of data access, without compromising data security. In its simplest terms: Data federation is a software process that enables numerous databases to work together as one. Using this technology is highly relevant for accessing sensitive biomedical health data, as the data remains within appropriate jurisdictional boundaries, while metadata is centralised and searchable and researchers can be virtually linked to where it resides for analysis.
This is an alternative to a model in which data is moved or duplicated then centrally housed - when data is moved it becomes vulnerable to interception and movement of large datasets is often very costly for researchers.
- Federated architectures of individual organisations may be connected together into a federated data platform, enabling data access for users across organisations.
- Federated data analysis takes access a step further and brings approved researcher’s analysis and computation to where the data resides. Federated data analysis allows researchers to analyse data across multiple distinct organisations in a secure manner.
With federation, data is never moved or copied. Security is maximised throughout data analysis and querying the data. There are other important advantages in using federated data analysis, which are summarised in the table below.
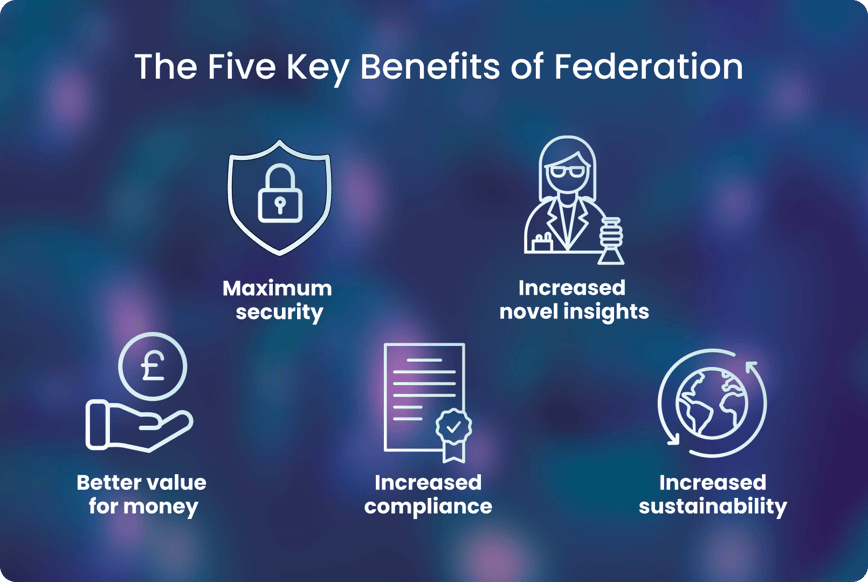
There are five key benefits of data federation
- Maximum security
-
Federated data analysis maximises security because data is never copied or moved. Organisations maintain full security controls over their data. Additionally, organisations can create permissioned-based access to guarantee that only the right people have access to the required data for their work.
- Increased novel insights
Federated data analysis enables the use of all available data to power insights. When disparate cohorts are combined to increase sample numbers, the studies increase their statistical power and findings. For example, one genome-wide association study revealed that increasing sample size by 10-fold led to an approximately 100-fold increase in findings, enabling disease-causing genetic variants of interest to be more easily validated and studied. Secure access to larger datasets via federation can help to accelerate research by providing great power for clinical studies.
- Better value for money
Expensive data copying and transferring are unnecessary when federated data analysis is performed, as the analysis is brought to the data. This limited data movement and storage results in lower costs for researchers and organisations.
- Increased compliance
Sensitive personal data such as healthcare data cannot traverse jurisdictional borders due to rising local, national, and international restrictions (eg GDPR). Federation enables organisations to fully comply with these rules because no data transfer or copying is necessary.
- Increased sustainability
Federated data access across cloud-based systems is the most resource-efficient and sustainable approach to securely accessing data since it minimises data duplication and does not require file transfers.
Data federation can ultimately help democratise access to data and insights gained
The benefits of expanded security and decreased costs that data federation brings serve to safely democratise valuable access to health and biomedical information, ultimately empowering researchers to share safely, access and collaborate over data worldwide.
In the cases of genomics, the majority of research undertaken to date focuses on populations of European heritage. This lack of diversity in genomics research is a serious problem because it can result in misdiagnosis, inadequate understanding of conditions, and inconsistent care delivery. As a result, not everyone benefits equally from genetic medicine. To boost confidence and encourage participation in research for underrepresented communities, a global, focused engagement effort alongside enhanced transparency and building public trust are needed.
Public and patient trust remains a key factor in participant recruitment, particularly for historically marginalised populations. In a federated data access model, the public’s data remains in the secure control of the data custodian, which could help engender increased trust. However, it is crucial that data access agreements must be negotiated in a manner that is acceptable for research participants, particularly in historically underrepresented, marginalised or vulnerable groups.
It is also possible that federated platforms, with their associated benefits of lower cost, could help make big data analytics more accessible to lower and middle income countries. Additionally, this could help improve diversity of the cohorts that can be built and accessed via federated networks.
Ultimately, data federation can help democratise data access and promote global collaboration to help ensure equitable benefits sharing
Summary
In summary, data federation can bring many wide ranging benefits to researchers. It can provide secure access to global cohorts of data to help power their analysis, answer important research questions and lead to scientific discovery. Federated data analysis offers maximum value for money as costly data transfers are avoided. Ultimately, data federation can help democratise data access and promote global collaboration to help ensure equitable benefits sharing.
Look out for the next blog in our series where we will take a detailed look into the key technical requirements that are required for organisations to enable data federation.
Author: Hannah Gaimster, PhD
Contributors: Hadley E. Sheppard, PhD and Amanda White
About Lifebit
At Lifebit, we develop secure federated data analysis solutions for clients including Genomics England, NIHR Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre, Danish National Genome Centre and Boehringer Ingelheim to help researchers turn data into discoveries.
Interested in learning more about Lifebit’s federated data solution?