7 clinical challenges surrounding health data standardisation (and how to overcome them)

Introduction to health data standardisation
Understanding the clinical challenges in health data standardisation is essential for maximizing the potential of these datasets.
The clinical challenges in health data standardisation are at the forefront of health research.
Understanding the clinical challenges in health data standardisation is crucial to address the growing volume of health data.
The amount of health data required to address critical questions continuously grows in research and healthcare. New technologies have made it possible to create large health datasets, collected from all over the world and across numerous organisations. These technologies include digitising medical tools, accumulating electronic health records (EHRs), and lower-cost genome sequencing.
These vast datasets can provide important insights that may ultimately enhance lives. Recent groundbreaking studies that illustrate the power of big data in health research include:
- the 100,000 Genomes study on rare diseases.
- research reporting the host characteristics triggering severe COVID-19 on approximately 60,000 participants.
- research confirming that high blood pressure is a risk factor for dementia– here, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) All of Us database of EHRs on +125,000 participants was utilised.
However, to be able to use all this valuable data in analysis, it must first be standardised and made interoperable in order to accurately combine data from multiple sources.
This article specifically focuses on the clinical challenges associated with health data transformation, and the solutions to connect high quality datasets, to inform clinical decision making and progress life sciences research.
To tackle the clinical challenges in health data standardisation, data must be made interoperable.
This article delves into the clinical challenges in health data standardisation and potential solutions.
What are the challenges surrounding clinical data standardisation?
Addressing the clinical challenges in health data standardisation is vital for improving patient outcomes.
Health data transformation is crucial for ensuring consistency, interoperability, and quality of data across different systems and institutions. However, there are several challenges that include:
These challenges highlight the need for effective clinical challenges in health data standardisation.
- Diverse data sources
Clinical data originates from various sources, including different collection sites, EHR systems, medical devices, and more. These sources may use different data models, schemas, and formats for clinical data collection. This makes it challenging to integrate and standardise the data. - Data volume and complexity
Healthcare organisations often have vast amounts of data to process (terabytes in volume), which can include structured data (eg lab results) and unstructured data (eg clinical notes). - Data heterogeneity
Health data is documented in different formats, languages, and units. Standardising units of measurement, terminologies, and health codes is a challenge, especially when dealing with data from different organisations and geographic regions. - Interoperability
Designing interoperable application programming interfaces (APIs) that allow different health systems to communicate and seamlessly exchange standardised data is technically challenging. Ensuring these APIs are well-documented and adhere to industry standards is crucial. - Quality and consistency
When clinical data is standardised, ensuring data quality and consistency is essential. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to erroneous clinical or research decisions. - Evolving standards
Healthcare data standards and terminologies are continually evolving to accommodate new knowledge, technology advancements, and changes in healthcare practices. It is crucial to keep up with these changes, although time consuming. - Security and privacy
When standardising clinical data, organisations must maintain patient privacy and adhere to data security regulations (eg HIPAA). Further, moving the data to provide third party access ultimately increases the security risks.
Efforts to understand the clinical challenges in health data standardisation can lead to better integration.
The quality of data is affected by clinical challenges in health data standardisation.
Organizations must adapt to the clinical challenges in health data standardisation to remain competitive.
Addressing evolving clinical challenges in health data standardisation requires ongoing training.
The identification of clinical challenges in health data standardisation is crucial for policy making.
Utilizing common data models can help address clinical challenges in health data standardisation.
Identifying solutions to connect high-quality datasets
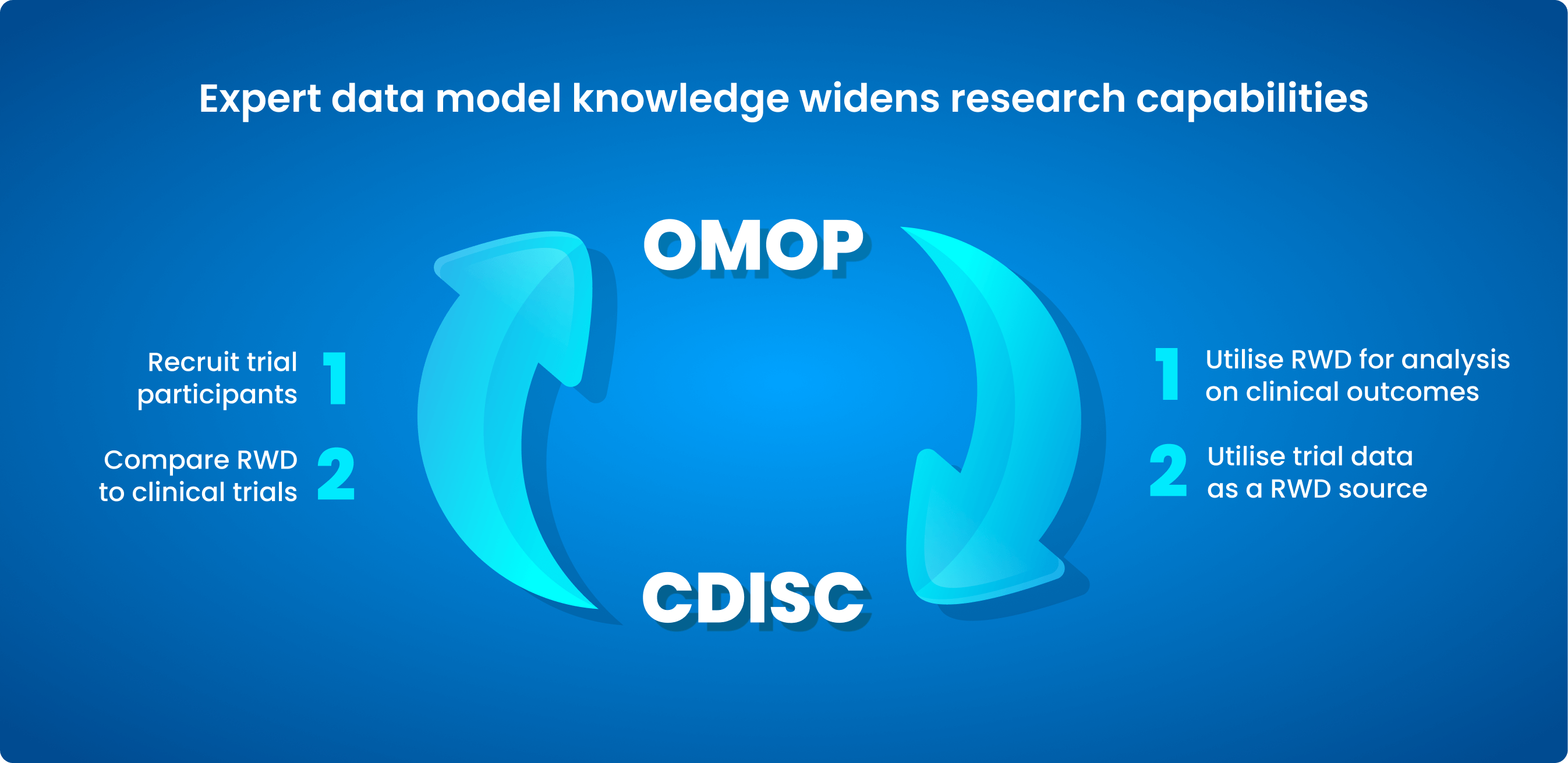
Common Data Models (CDMs) are being increasingly utilised in the healthcare sector to overcome the lack of consistency in health data. Collaborative health research on data across nations, sources, and systems is made possible by the standard approach. Examples include the Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership (OMOP) CDM and Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC) medical standards.
What is OMOP?
CDISC standards play a role in mitigating clinical challenges in health data standardisation.
OMOP is an open community data standard created to standardise observational data formats and content and to facilitate quick analyses. The OHDSI standardised vocabulary is a key part of the OMOP CDM. The OHDSI vocabularies enable standard analytics and allow the organisation and standardisation of medical terms to be used across the various clinical domains of the OMOP CDM.
Research shows that clinical challenges in health data standardisation can impact health outcomes.
What is CDISC?
By focusing on clinical challenges in health data standardisation, researchers can drive innovation.
CDISC creates data standards for the gathering, analysing, and sharing of clinical trial data in conjunction with a wide spectrum of international professionals. Researchers, pharmaceutical and biotech firms, governmental organisations (such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), and the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA)), and technology suppliers all utilise CDISC standards. The standards help to make data more easily accessible, interoperable, and reusable so that clinical research and global health can be improved.
| CDISC | OMOP | |
| Type of data | Clinical trial data | Observational data |
| Mode of collection | Collected via an experiment | Collected through real-world settings |
| Size of data | Small size (megabytes) | Gigantic (terabytes) |
| Use of data | Collected for the purpose of running a clinical trial | Collected for multiple research use cases |
Addressing clinical challenges in health data standardisation involves collaboration among stakeholders.
Effective strategies to overcome clinical challenges in health data standardisation are essential.
Continuous improvement in clinical challenges in health data standardisation will lead to better decision making.
Featured resource: Read our whitepaper on Lifebit’s approach to data standardisation
To leverage a breadth of health data types, both clinical trial and non-clinical trial health data, researchers must transform these datasets to CDMs. However, this is time consuming and costly, with data scientists estimated to devote 80% of their work to organising and cleaning data.
Researchers should be able to spend time on what matters most – analysis that will derive meaningful insights to benefit the lives of patients.
To empower researchers to effectively collaborate over their data, industry providers are now offering support services for the standardisation of data to CDMs. This saves researchers’ time and effort, with providers offering fully-dedicated, expert teams that have developed proprietary ETL pipelines to streamline the standardisation process while maintaining data quality standards. Working with providers who are experts in both the standardisation of clinical trial and observational data types can help connect these datasets for a variety of use cases, powering clinical and research breakthroughs.
Finally, throughout the process of data standardisation, data security and patient privacy should always remain a primary concern.
When data is moved, for example to provide to an industry partner to standardise the data, it can become vulnerable to interception (and furthermore the movement of large datasets is often very costly). Trusted research environments and data federation allow virtual access to the data through Application Program Interfaces (APIs), avoiding moving or copying the data.
By using this approach, data can be standardised and made interoperable for collaborative research without compromising security.
Summary
Health data comes from various sources and exists in multiple formats. Combining this data to gain novel insights can only be achieved if the data is made interoperable. Standardising health datasets requires overcoming clinical challenges related to resources, technological capabilities and data governance to safely empower data consumers to maximise research insights and discoveries.
Look out for the next blog in our series, where we will describe further, specific benefits that standardisation of health data can bring to researchers and clinicians.
Once data is standardised, users can bring standardised analytical tools to where the data resides in its secure environment. However, access to and analysis of the data must also be harmonised to maximise insights that can be gained.
About Lifebit
Lifebit provides health data standardisation services for clients, including Genomics England, Boehringer Ingelheim, Flatiron Health and more, to help researchers transform data into discoveries.
Lifebit’s services are making health data usable quickly.
Find out more about the value of data standardisation at our upcoming webinar, Data Harmony, on 14 September 2023. Secure your place today.

