The Remote Clinical Trial Monitoring Survival Guide

Remote clinical trial monitoring: 4 Step Survival
Why Remote Clinical Trial Monitoring Has Become Essential
Remote clinical trial monitoring has transformed from an emergency pandemic solution to the new industry standard. Here’s what you need to know:
Key Methods of Remote Clinical Trial Monitoring:
- Remote Source Data Verification (rSDV) – Verify source data remotely through secure platforms
- Centralized Monitoring – Analyze data trends across multiple sites from a central location
- Risk-Based Monitoring (RBM) – Focus resources on high-risk areas using data analytics
- Hybrid Models – Combine remote oversight with strategic on-site visits
- Real-time Data Review – Monitor patient safety and protocol compliance continuously
The shift was rapid: by early 2021, 97% of clinical trial sponsors used remote data review. The results are clear: remote monitoring saves CRAs up to 7.5 hours per week in travel and enables them to monitor 2-5 sites weekly, up from just one. Beyond efficiency, the COVID-19 pandemic proved remote monitoring improves data integrity and patient safety. Sites could identify deviations and adverse events faster, providing more consistent oversight than traditional on-site visits ever allowed.
The technology stack has also evolved rapidly, with modern platforms integrating electronic Investigator Site Files (eISFs), real-time data from wearables, and AI-powered analytics. Yet many organizations still struggle with implementation, facing regulatory compliance questions, site resistance, and data privacy concerns.
I’m Maria Chatzou Dunford, CEO of Lifebit. With over 15 years developing federated data platforms for secure remote clinical trial monitoring, my experience has shown me how the right technology can transform clinical oversight from a burden into a competitive advantage.
Handy remote clinical trial monitoring terms:
- decentralized clinical trial model
- decentralized clinical trials guidance
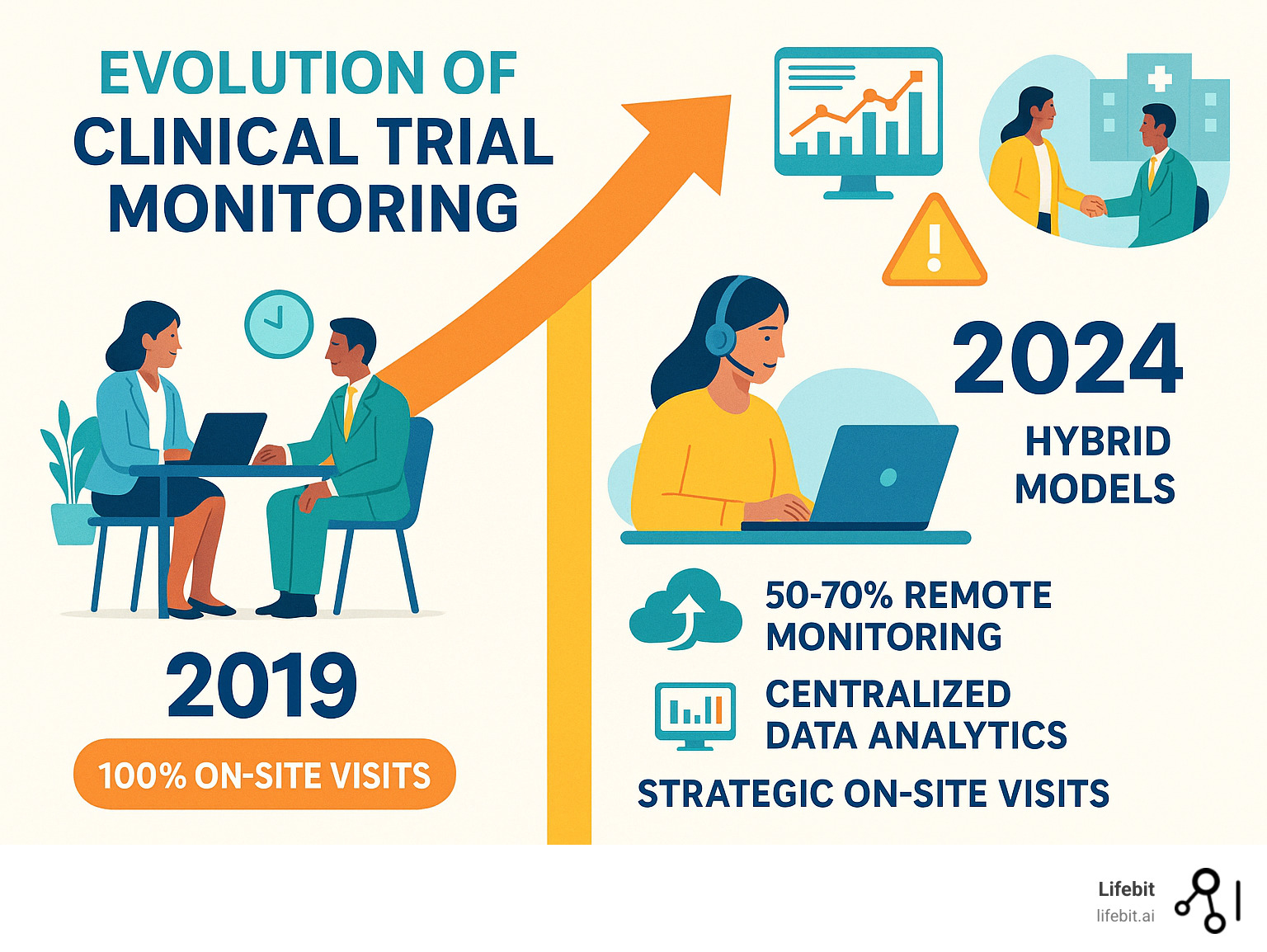
The Evolution of Clinical Trial Monitoring: From On-Site to Remote
For decades, clinical trial monitoring meant one thing: Clinical Research Associates (CRAs) packing their bags and hitting the road. This on-site model was the gold standard for ensuring trial safety and integrity. However, this old way of doing things was already showing cracks long before the pandemic.
Traditional On-Site Monitoring: The Old Standard
On-site, a CRA would spend days performing 100% Source Data Verification (SDV)—carefully checking every data point against source documents. These on-site visits were vital for building relationships with site staff and observing the trial environment.
But the numbers tell a sobering story. CRAs spent 18% of their time traveling, nearly a full day each week. The costs were staggering, and the inefficiencies were becoming impossible to ignore as trials grew larger and more complex.
The Catalyst for Change: Pandemic Pressures and Pre-existing Inefficiencies
COVID-19 brought trials to a screeching halt in March 2020. Travel restrictions and lockdowns meant CRAs couldn’t get to sites. With a sponsor losing $600,000 to $8 million per day from delays, the industry faced a stark choice: adapt or fail.
The pandemic forced everyone’s hand, revealing that many monitoring activities didn’t require physical presence. Trial continuity became the driving force for innovation, proving that remote clinical trial monitoring wasn’t just a temporary workaround—it was often more efficient and effective.
What emerged wasn’t a wholesale replacement of on-site monitoring, but a smarter, more strategic approach that combined the best of both worlds.
Understanding Modern Monitoring Methods
Today’s monitoring toolkit is diverse, allowing strategies to be custom to each trial’s needs.
Remote Monitoring lets CRAs review documents and data through secure platforms without traveling to sites. This maintains oversight while dramatically cutting costs and time.
Centralized Monitoring takes a bird’s-eye view. Centralized teams analyze data patterns across multiple sites simultaneously, spotting trends and outliers that might be invisible to someone focused on a single location.
Remote Source Data Verification (rSDV) brings the rigor of traditional source data checking into the digital age. Specialized teams can verify source data remotely through secure access to electronic health records and scanned documents.
Risk-Based Monitoring (RBM) has transformed oversight entirely. Instead of checking everything with equal intensity, RBM focuses resources where they matter most.
These modern methods work best when combined thoughtfully. A well-designed remote clinical trial monitoring strategy might use centralized monitoring to identify issues, remote monitoring for routine oversight, and strategic on-site visits for complex problem-solving. The result? Trials that are monitored more consistently and effectively than ever before.
Mastering Your Remote Clinical Trial Monitoring Strategy
Building a successful remote clinical trial monitoring strategy isn’t just about buying new software. It requires a solid plan that combines smart technology with human expertise, considering your unique trial requirements, site capabilities, and regulatory obligations. Here’s a step-by-step guide to building that blueprint.
Step 1: Conduct a Comprehensive Risk Assessment
Every successful strategy starts with Risk-Based Monitoring (RBM) to understand what could go wrong and where to focus your energy, as mandated by ICH E6(R2). The process begins with identifying critical data and processes, like primary endpoints and informed consent. Next, you assess risks at the system and site level, considering factors like trial complexity and site experience. The core of modern RBM involves establishing Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) and Quality Tolerance Limits (QTLs). KRIs are metrics that signal potential issues (e.g., high screen failure rates), while QTLs define the acceptable range. When a KRI crosses a QTL threshold, it triggers a pre-defined action, like a targeted remote review or an on-site visit. This data-driven approach transforms monitoring from a routine checklist into a dynamic, responsive system focused on patient safety and data integrity.
More on innovations in clinical trial design
Step 2: Choose the Right Technology Stack
The right technology can provide a competitive advantage. Electronic Investigator Site Files (eISFs) are game-changers. Site-owned eISFs give research sites control while granting sponsors secure access, a win-win that builds trust. That’s why 78% of sponsors planned to use a site-friendly eISF for remote monitoring in 2023.
Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems move you away from paper, with real-time data entry and validation catching errors early. Secure data access platforms are the backbone of remote monitoring, providing controlled, auditable access for CRAs.
Finally, wearables and real-world data integration provide a complete picture of how treatments work through continuous, objective data collection. Our federated AI platform brings these pieces together, providing secure, real-time access to global biomedical data with built-in harmonization and advanced analytics capabilities. Components like our Trusted Research Environment (TRE), Trusted Data Lakehouse (TDL), and R.E.A.L. (Real-time Evidence & Analytics Layer) deliver the real-time insights and AI-driven safety surveillance that modern remote clinical trial monitoring demands.
Explore modern Clinical Research Technology
Step 3: Implement a Hybrid Monitoring Model
The most effective strategies aren’t 100% remote. The sweet spot is a hybrid model that combines the efficiency of remote activities with strategic, high-value on-site visits. Remote Source Data Review (SDR) and Remote Source Data Verification (rSDV) can handle the heavy lifting of document reviews and data checks more efficiently from a central location.
Strategic on-site visits remain crucial, but are now more focused on building relationships, observing processes, and handling tasks that genuinely require physical presence. The Beijing Cancer Hospital case study illustrates this balance: their hybrid model increased patient visit reviews by 34%, decreased monitoring duration by 13.8%, and reduced total monitoring costs by 46.2%.
Step 4: Ensure Site Readiness and Reduce Burden

Even the best technology is useless if sites don’t adopt it. Success depends on making the transition smooth for site staff. Comprehensive site training and support is crucial, including on-demand modules and a dedicated technical support line. Standardized workflows should be practical and developed with site input. Automated PHI redaction capabilities are non-negotiable for rSDV, as manual redaction is a major site burden and risk. This technology must be validated for compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. Finally, maintain proactive communication channels using secure video calls and collaborative platforms. Empowering ‘site champions’—tech-savvy staff who advocate for new workflows—can also dramatically accelerate adoption and build a true partnership.
The Impact and Benefits of Going Remote
The change to remote clinical trial monitoring isn’t just about keeping up with technology trends. It’s about fundamentally improving how we conduct clinical research, making trials more efficient, cost-effective, and ultimately better for patients.
Think about it: we’re talking about a complete shift from the old days of CRAs lugging suitcases from airport to airport, spending more time in transit than actually monitoring data. Now, with the right technology and approach, we can deliver better oversight while reducing costs and improving patient safety. Let me walk you through what this looks like in practice.
Boosting Efficiency and Slashing Costs
The numbers tell a compelling story about what happens when we accept remote clinical trial monitoring. We’re seeing real, measurable improvements that directly impact trial timelines and budgets.
Travel time savings are just the beginning. CRAs used to spend nearly a fifth of their work week traveling between sites. With remote monitoring, they’re saving up to 7.5 hours per week that can be redirected to meaningful work like deeper data analysis or supporting struggling sites. That’s almost a full workday back in their schedule every week.
But here’s where it gets really interesting: increased monitoring frequency changes the entire game. When travel barriers disappear, CRAs can check in with sites more often. The contrast is stark – 52% of CRAs could only monitor one site per week with traditional methods, but 75% now monitor 2-5 sites per week with remote capabilities. This isn’t just about efficiency; it’s about catching issues before they become problems.
Document review becomes dramatically faster too. What used to take over 7 hours of on-site document review now typically takes 3-4 hours remotely. This speed improvement means 78% of CRAs can move documents into the eTMF faster, keeping regulatory files current and complete.
The ripple effects are impressive. 75% of CRAs can identify potential risks with site documents earlier, and 68% can remediate document issues faster. When you can spot protocol deviations or data quality issues within days instead of weeks, you prevent small problems from snowballing into major complications.
The bottom line impact is substantial. Site Enablement Platforms that support remote clinical trial monitoring can accelerate clinical trials by six weeks and reduce costs by over $1M per study. For an industry where delays can cost sponsors between $600,000 to $8 million per day, these improvements represent game-changing value.
Enhancing Data Integrity and Patient Safety
Beyond the obvious cost and time benefits, remote clinical trial monitoring fundamentally improves the quality of clinical research. This isn’t just about working faster – it’s about working smarter to protect patients and ensure data integrity.
Real-time data access transforms oversight from periodic check-ins to continuous vigilance. Instead of waiting weeks or months between site visits to review data, monitors can access information as it’s collected. This constant visibility means potential safety signals or protocol deviations are spotted immediately, not at the next scheduled visit.
Centralized monitoring capabilities allow us to see patterns across multiple sites simultaneously. When you’re looking at aggregated data from all sites in real-time, systemic issues become obvious. Maybe one site is consistently reporting lower adverse event rates than others, or there’s a pattern of protocol deviations across multiple locations. These trends would be invisible to individual CRAs visiting sites separately.
Patient safety gets a significant boost because adverse events are detected and reported faster. Patients often have 24/7 access to study team members through digital platforms, unlike traditional site-based approaches where communication might be limited to business hours. When patients can report symptoms or concerns immediately, and that information flows directly to monitors, we can respond to safety issues in real-time.
The continuous oversight model means we’re proactively preventing problems rather than reactively fixing them. This constant vigilance directly contributes to higher data quality throughout the trial lifecycle.
Our platform’s Trusted Research Environments are specifically designed to secure Clinical Trial Patient Data while enabling this level of access and oversight. We ensure data remains protected and compliant while being readily available for monitoring activities.
Overcoming the Challenges of remote clinical trial monitoring
Let’s be honest – implementing remote clinical trial monitoring isn’t without its problems. But understanding these challenges upfront allows us to address them strategically and build more robust programs.
Data privacy and security concerns top the list of challenges. When sharing patient data remotely, compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and other privacy regulations is non-negotiable. This requires a multi-layered strategy. Legally, it involves specific patient consent for remote access and clear data processing agreements (DPAs). Technologically, platforms must feature role-based access controls (RBAC), end-to-end encryption, and immutable audit trails. The HIPAA Privacy Rule, for example, requires specific patient authorization before protected health information (PHI) can be shared with remote monitors. Our federated AI platform addresses these concerns through built-in federated governance, allowing insights to be generated without requiring data transfer, thus minimizing data movement and risk.
Technology adoption barriers can slow implementation, especially at sites that aren’t comfortable with new digital workflows. Some staff resist change, worry about increased data entry burden, or simply lack training on new systems. We tackle this through comprehensive training programs, intuitive user interfaces, and ensuring new systems integrate seamlessly with existing site technologies to avoid duplicate work.
Site burden concerns often arise initially, particularly when sites think they’ll need to scan and upload documents or manage additional software. We address this by advocating for site-owned eISFs, providing robust technical support, and demonstrating how remote monitoring ultimately reduces administrative load over time.
The lack of physical oversight remains a legitimate limitation. Remote monitoring excels at data review, but CRAs can’t physically observe processes or assess facility conditions through a screen. This is precisely why hybrid models are the gold standard. They reserve strategic on-site visits for high-value activities requiring physical presence. These include initial site initiation, observing complex procedures like informed consent, inspecting investigational product storage, and resolving sensitive issues in person. By handling routine data verification remotely, these on-site visits become more focused and impactful, strengthening the sponsor-site partnership.
By acknowledging these challenges and building solutions around them, we create remote clinical trial monitoring programs that maximize benefits while minimizing friction for everyone involved.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape and Future Trends for Remote Clinical Trial Monitoring
The rapid evolution of remote clinical trial monitoring has been closely mirrored by progressive changes in regulatory guidance. Furthermore, the future promises even deeper integration with cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence and real-world data.
The Regulatory Green Light for remote clinical trial monitoring
Regulatory bodies worldwide have not only acknowledged but actively encouraged the adoption of remote clinical trial monitoring. This has provided a crucial framework for sponsors and CROs to confidently implement these new strategies.
- FDA Guidance: The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has been a key proponent. Their 2013 guidance, “Oversight of Clinical Investigations — A Risk-Based Approach to Monitoring,” moved away from the expectation of 100% SDV, promoting a more targeted approach. More recently, the “FDA Guidance on Conduct of Clinical Trials of Medical Products during COVID-19 Pandemic” explicitly stated that if on-site visits were not feasible, trial sponsors should consider centralized or remote clinical trial monitoring approaches to maintain oversight. In December 2021, the FDA even issued draft guidance on digital tools for remote data acquisition in decentralized trials, signaling a clear push towards greater adoption.
- EMA Guidance: Similarly, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has encouraged flexible monitoring strategies. Their 2013 “Reflection paper on risk-based quality management in clinical trials” emphasized monitoring as a function of Good Clinical Practices (GCP). During the pandemic, the EMA’s “Guidance on the Management of Clinical Trials During the COVID-19 (Coronavirus) Pandemic” explained that they would consider remote site data verification (SDV) for trials related to COVID or those meeting significant unmet medical needs.
- ICH Guidelines: The International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) has also updated its foundational guidelines to support modern monitoring. ICH E6(R2), an integrated addendum to the Good Clinical Practice guideline, promoted a more risk-based approach to monitoring. The forthcoming ICH E8(R1) and the draft ICH E6(R3) are designed to be media-neutral, encouraging the use of various technologies and innovative designs, including the integration of Real-World Data (RWD). This international harmonization is crucial for global trials.
These regulatory endorsements provide a solid foundation, allowing sponsors, sites, and CROs to adopt remote clinical trial monitoring while adhering to all necessary standards.
FDA Guidance on Conduct of Clinical Trials
EMA guidance on risk-based quality management
The Future is Federated: AI and Real-World Data Integration
The trajectory for remote clinical trial monitoring points towards increasingly sophisticated integration with artificial intelligence (AI) and the vast potential of real-world data.
- AI for Anomaly Detection and Predictive Analytics: AI and machine learning are changing how we analyze clinical data. They can rapidly identify anomalies, predict potential risks, and highlight areas requiring closer attention, far beyond what human monitors can achieve manually. This includes spotting patterns in data that might indicate a site issue, a potential safety signal, or even a recruitment challenge. Our platform, with its advanced AI/ML analytics, is designed to provide these deep insights, enabling proactive decision-making.
- Real-World Data (RWD) and Decentralized Clinical Trials: The growing acceptance and availability of RWD from sources like electronic health records (EHRs) and wearables are changing the landscape. Remote clinical trial monitoring is a natural fit for decentralized clinical trials (DCTs), which often rely heavily on remote data collection from patients in their homes. This allows for a more patient-centric approach, bringing trials closer to participants and broadening recruitment reach.
- Federated Learning: As clinical trial data becomes more distributed across various healthcare systems and geographies, federated learning emerges as a powerful solution. This approach allows AI models to be trained on diverse datasets located at their source, without the data ever having to leave its secure environment. This is particularly relevant for remote clinical trial monitoring in global contexts, as it addresses data privacy concerns while enabling collaborative research. Our federated AI platform is at the forefront of this innovation, enabling secure, real-time access to global biomedical and multi-omic data for compliant research and pharmacovigilance across different entities, including governments and public health agencies. This secure collaboration across hybrid data ecosystems is what truly defines the future of remote clinical trial monitoring.
The role of AI for Clinical Trials
How Trusted Research Environments enable secure data collaboration
Conclusion: Remote Monitoring is the New Standard
The change of remote clinical trial monitoring from emergency pandemic solution to industry standard has been remarkable. What started as a desperate pivot during COVID-19 lockdowns has become the foundation of modern clinical research.
Think about where we were just a few years ago. CRAs spent nearly one-fifth of their time traveling between sites, armed with sticky notes to verify paper records. Sites dreaded the disruption of monthly monitoring visits. Trial delays cost sponsors millions per day, yet the traditional model seemed unchangeable.
The pandemic forced our hand, but the results spoke for themselves. Remote clinical trial monitoring didn’t just maintain data quality – it improved it. CRAs could suddenly monitor multiple sites per week instead of just one. Issues were caught faster. Costs dropped dramatically. The Beijing Cancer Hospital study showed us the numbers: 46% cost reduction and 34% more patient visits reviewed with their hybrid approach.
Hybrid models have emerged as the clear winner, combining the efficiency of remote oversight with strategic on-site visits. It’s not about choosing between remote and traditional monitoring anymore – it’s about using each approach where it works best.
The benefits keep stacking up. CRAs save 7.5 hours weekly that used to be spent traveling. 75% can now monitor 2-5 sites per week remotely. Real-time data access means adverse events get spotted sooner, and protocol deviations don’t fester for weeks between visits. Sites appreciate the reduced disruption, and sponsors love the cost savings that can exceed $1 million per study.
Yes, challenges remain. Data privacy concerns are real – HIPAA waivers and GDPR compliance aren’t optional. Some sites still struggle with technology adoption. But these problems are getting smaller as platforms become more intuitive and training improves.
The regulatory landscape has shifted decisively in favor of remote clinical trial monitoring. The FDA, EMA, and ICH guidelines all encourage risk-based, technology-enabled approaches. We’re not operating in a regulatory gray area anymore – we have clear guidance supporting these methods.
Looking ahead, the integration of AI and real-world data will make remote clinical trial monitoring even more powerful. Imagine AI systems that can spot data anomalies across thousands of patients instantly, or wearables that provide continuous safety monitoring without any site visits. Federated learning will let us analyze global datasets while keeping sensitive information secure in its home environment.
At Lifebit, we’re building the infrastructure that makes this future possible. Our federated AI platform provides the secure, real-time data access that next-generation remote clinical trial monitoring demands. With components like our Trusted Research Environment and R.E.A.L. analytics layer, we’re helping biopharma companies, governments, and public health agencies conduct more efficient, compliant research.
Remote clinical trial monitoring isn’t just the new standard – it’s the foundation for everything coming next in clinical research. The question isn’t whether to adopt it anymore, but how quickly you can implement it effectively.
Learn how Lifebit’s platform can power your next-generation clinical trials

