The AI Doctor Will See You Now: Personalized Medicine’s Next Frontier

Why AI in Personalized Medicine Changes Everything
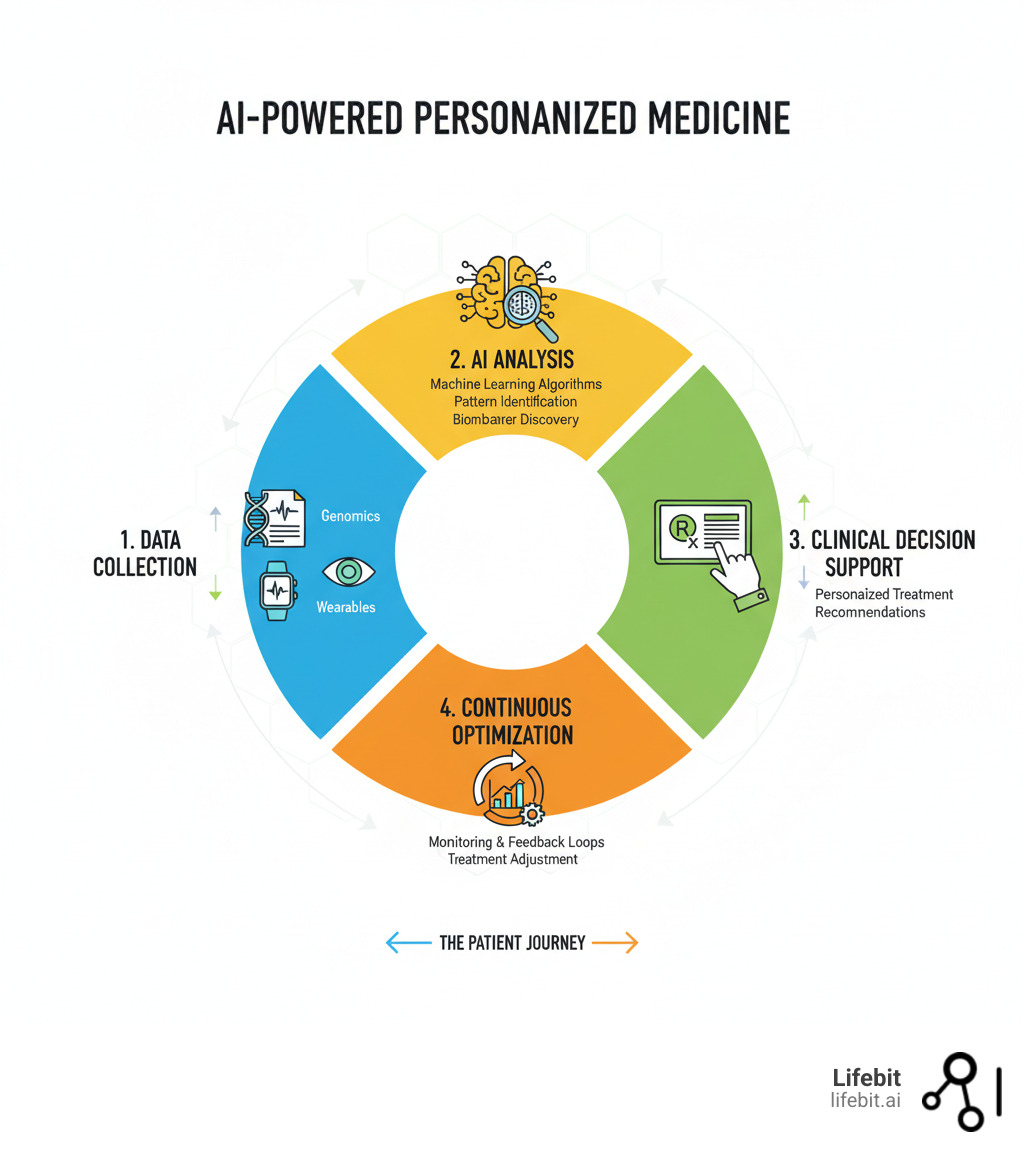
For centuries, medicine has operated on the principle of the “average patient,” developing drugs and treatments that work for the largest number of people. However, this one-size-fits-all model fails individuals who fall outside the average, leading to ineffective treatments and unpredictable side effects. For example, a standard dose of a common blood thinner may be perfect for one person but cause dangerous bleeding in another due to a subtle genetic difference. AI in personalized medicine dismantles this outdated paradigm. It is revolutionizing healthcare by analyzing your unique genetic, clinical, and lifestyle data to tailor treatment plans specifically for you—not for a statistical mean. By leveraging machine learning, AI can steer complex genomic datasets, identify subtle patterns, and predict drug responses with unprecedented accuracy.
Key applications include:
- Drug Response Prediction: Analyzing genomic data to predict which medications will work best for your genetic profile. This field, known as pharmacogenomics, uses AI to scan for variants in genes like the Cytochrome P450 family, which are crucial for metabolizing over 70% of clinically used drugs.
- Early Disease Detection: Identifying high-risk patients years before traditional assessments. By integrating genomic risk scores with subtle changes in clinical data over time, AI can flag individuals at high risk for conditions like Alzheimer’s, type 2 diabetes, or certain cancers, opening a window for preventive intervention.
- Precision Dosing: Optimizing drug dosages based on genetic markers to reduce adverse reactions. Instead of standard dosing, AI models can recommend a starting dose based on an individual’s predicted drug metabolism rate, minimizing trial and error.
- Multi-Omic Integration: Fusing genomics, proteomics, clinical records, and wearable data into comprehensive health profiles. This means AI doesn’t just look at your DNA; it connects it with your gene activity (transcriptomics), protein functions (proteomics), and metabolic state (metabolomics) for a truly holistic view.
- Clinical Decision Support: Providing real-time treatment recommendations by analyzing complex biological data. These systems act as an expert assistant for clinicians, highlighting potential diagnoses or suggesting treatment pathways based on the latest evidence and the patient’s unique data.
For decades, personalized medicine remained largely theoretical due to the sheer complexity of genomic data. AI has made it a reality. For example, AI models have demonstrated 71.8% superiority over conventional methods in predicting outcomes for urologic disorders and have outperformed specialists in detecting retinal fluid.
This technology is shifting healthcare from reactive treatment to proactive, predictive, and preventive care. It moves us beyond a “one-size-fits-all” approach to precision medicine that recognizes you as an individual.
I’m Maria Chatzou Dunford, CEO and Co-founder of Lifebit. For over 15 years, I’ve focused on advancing AI in personalized medicine through federated genomic data analysis. My work bridges computational biology, AI, and secure biomedical data integration to make personalized treatment a reality for patients worldwide.
While the convergence of AI and personalized medicine is accelerating, significant challenges in data privacy, algorithmic bias, and implementation remain. This guide explores how AI is revolutionizing healthcare, the technologies making it possible, and the critical challenges we must overcome.
Must-know ai in personalized medicine terms:
- Integrating Multi-Modal & Genomic and Multi-Omics Data for Precision Medicine
- Who provides advanced analytics solutions for multi-omic data?
How AI Decodes Your DNA to Predict Drug Reactions
Your DNA holds the blueprint for how your body responds to medications. This field, known as pharmacogenomics, has been a cornerstone of personalized medicine, but its clinical application was limited by the slow, laborious process of genetic analysis. AI in personalized medicine solves this by processing vast genomic data in hours, not months. It can rapidly identify well-known genetic markers, such as variants in the TPMT gene that predict severe reactions to thiopurine drugs used in chemotherapy, or the HLA-B5701* allele that signals a high risk of a dangerous hypersensitivity reaction to the HIV drug abacavir. By automating this analysis, AI makes it feasible to screen patients proactively, ensuring they receive a drug that is not only effective but also safe for their specific genetic makeup.
AI is also accelerating drug development. By predicting efficacy and safety early, AI helps identify promising drug targets and design more efficient clinical trials. This has also enabled drug repositioning—finding new uses for existing medications based on individual patient profiles. By screening libraries of existing compounds against complex biological models of a disease, AI can identify unexpected therapeutic matches, offering a faster, more cost-effective path to new treatments. Scientific research on AI in pharmacogenomics highlights how these AI-driven approaches are changing pharmaceutical development.
Multi-omics data integration improves this process. AI combines genomics with transcriptomics (gene activity), proteomics (proteins), and metabolomics (metabolites) to create a comprehensive biological picture. This holistic view reveals patterns invisible in a single data type, leading to more accurate drug response predictions and better biomarker identification.
Using AI algorithms to analyze complex genomic data
Machine learning and deep learning algorithms excel at finding subtle patterns in genomic data. For example, deep learning models can identify genetic variations from DNA sequencing data with greater accuracy than traditional methods, spotting the tiny changes in your genetic code that can dramatically affect drug response. For instance, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), originally designed for image analysis, have been adapted to “read” DNA sequences and identify patterns associated with disease risk or drug response. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are used to analyze sequential data, such as electronic health records over time, to predict disease progression.
Other advanced AI models can predict whether a genetic variant will cause disease. This is particularly crucial for reclassifying Variants of Uncertain Significance (VUSs)—genetic changes where the impact on health is unknown. A VUS can leave patients and doctors in a state of uncertainty for years. AI models, trained on massive databases of known pathogenic and benign variants, can predict the likelihood that a VUS is disease-causing, turning an ambiguous result into an actionable clinical insight. AI can also predict how genetic variants affect processes like alternative splicing (where one gene creates different proteins) and detect larger genetic changes like copy number variations, both of which significantly impact drug metabolism and treatment success.
For immunotherapy, AI models can predict immune responses, which is essential for designing personalized vaccines and treatments that work with a patient’s specific immune system.
The role of ai in personalized medicine for drug development
By integrating your genetic profile, clinical history, and lifestyle factors, AI builds comprehensive treatment models that predict your response to different therapies. This shifts medicine from a trial-and-error approach to a predictive one where the right treatment is chosen from the start.
A key benefit is predicting adverse drug reactions. AI analyzes genetic markers that influence drug metabolism to recommend precise dosages, reducing side effects and ineffective treatments. At Lifebit, our platform ensures this complex analysis happens securely within Trusted Research Environments, protecting patient data while enabling powerful insights.
AI also maps nonlinear variable interactions—the complex ways biological and clinical factors influence each other. In clinical trials, AI optimizes the process by identifying patient subgroups most likely to benefit from a new drug, increasing success rates and getting treatments to patients faster.
AI in the Clinic: Slashing Diagnosis Times and Tailoring Treatments

Imagine a doctor who can instantly compare your case against millions of others and spot warning signs years before symptoms appear. This is what happens when AI in personalized medicine assists your care team. By analyzing your genetic profile, medical history, and real-time data, AI creates a comprehensive health view, flagging potential adverse drug reactions and enabling proactive adjustments.
In Intensive Care Units, AI continuously monitors patients and predicts complications like organ failure, giving medical teams precious time to intervene. The impact is profound: a machine learning model was able to identify patients needing autoimmune disease testing up to 5 years before traditional clinical assessments. This shift from reactive treatment to proactive prevention is a core benefit of AI. A machine learning model for early autoimmune testing demonstrates this capability.
AI acts as a powerful ally for clinicians, processing information faster and spotting hidden patterns, leading to swifter diagnoses and more effective, personalized treatments.
Changing diagnosis and treatment in specific fields
The impact of AI in personalized medicine is changing medical specialties with more precise, individualized treatments.
- Oncology: AI analyzes tumor genomics to develop personalized treatment strategies. It can predict patient response to specific immunotherapies based on the tumor’s genetic signature. Furthermore, AI is transforming digital pathology, where algorithms analyze high-resolution images of tissue biopsies to identify cancer cells, determine tumor grade, and even spot mutations with an accuracy that can exceed the human eye. This is complemented by the analysis of liquid biopsies, where AI models detect and interpret fragments of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in the bloodstream to monitor treatment response and detect recurrence non-invasively.
- Cardiology: Machine learning models use health records and genetic data to predict cardiovascular events, allowing for early, targeted preventive care. AI algorithms can now analyze an electrocardiogram (ECG) in seconds to detect subtle signs of conditions like atrial fibrillation, even when the patient is not currently in an abnormal rhythm. Similarly, AI can analyze echocardiograms to automatically measure cardiac function and identify early signs of heart failure.
- Neurology: AI detects subtle signs of disease progression. For example, automated speech analysis can assess cognitive impairment in conditions like dementia. In addition, AI models can analyze MRI scans to detect patterns of brain atrophy indicative of Alzheimer’s disease years before significant cognitive decline becomes apparent, enabling earlier diagnosis and personalized monitoring.
- Rheumatology: AI integrates clinical, genomic, and immunological data to identify high-risk patients, predict disease flares, and optimize therapies for autoimmune diseases like Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Rare Diseases: For the millions suffering from rare diseases, the journey to a diagnosis—often called the “diagnostic odyssey”—can take an average of five to seven years. AI dramatically shortens this timeline. By combining genomic sequencing with AI-powered phenotype analysis (systematically analyzing a patient’s symptoms and physical traits), systems can compare a patient’s unique profile against vast databases of genetic diseases to propose a likely diagnosis in minutes.
How AI in personalized medicine improves medical imaging and telehealth
AI in personalized medicine also improves care through medical imaging and telehealth.
In medical imaging, AI-powered image recognition identifies details humans might miss. For instance, AI has shown superior accuracy to experts in identifying retinal fluid from OCT scans and has demonstrated 71.8% superiority in diagnostic prediction for urologic disorders.
The rise of digital health devices like smartwatches generates continuous health data. AI turns this data into actionable insights, enabling real-time monitoring and adjustments to personalized management plans. These digital biomarkers also support decentralized clinical trials.
Telehealth integration with AI democratizes access to personalized medicine. By analyzing patient-clinician interactions or augmenting diagnostic capabilities in resource-poor areas, AI makes specialized expertise more accessible, ensuring care is not just faster and more accurate, but also more personal.
Building Your Digital Twin: How AI Integrates All Your Health Data

A digital twin is more than a static snapshot; it is a dynamic, virtual replica of you, built from all your health data—from your DNA and medical records to data from your smartwatch. AI in personalized medicine makes this possible by fusing these once-siloed data streams into a single, unified health profile. This allows clinicians not only to monitor your current health but also to run simulations. For example, they could test the potential impact of a new medication or a change in diet on your virtual model before applying it in the real world, predicting efficacy and preventing potential harm.
This data fusion combines genomics, transcriptomics (active genes), proteomics (proteins), metabolomics (metabolism), clinical observations, medical imaging, and digital health indicators. The result is a comprehensive, real-time view of your health that allows clinicians to spot disease risks years earlier, predict drug responses before prescribing, and adjust treatments based on your body’s current state.
AI-driven analytics for a holistic health view
AI thrives on the complexity of integrated health data. By analyzing patterns across all sources, AI can predict health outcomes with remarkable accuracy. For example, combining genetic markers with clinical history and continuous data from a smartwatch—such as heart rate variability, sleep patterns, and activity levels—can create a highly accurate, personalized forecast for cardiovascular event risk, enabling precisely timed preventive interventions.
AI also excels at identifying potential risks by recognizing subtle warning signs across multiple data types that might otherwise be missed. It untangles nonlinear variable interactions—the complex ways genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors influence each other—to generate predictions that conventional methods cannot. The goal is a single, unified patient view that powers unprecedented insights. Learn more about multi-omics data analysis.
Novel applications of AI in personalized medicine
Integrating diverse data is opening new frontiers in research and care.
- Translational and Clinical Research: AI bridges the gap between lab findings and patient care by rapidly validating biomarkers against real-world patient data. It also makes clinical trials more efficient by identifying ideal patient candidates and analyzing trial data in real time for safety and efficacy signals.
- AI-enabled Immunology: The immune system is incredibly complex, but AI brings clarity. It uses dimensionality reduction techniques, like t-SNE and UMAP, to create intuitive visualizations of complex immune data, essentially turning a spreadsheet with thousands of columns into a simple 2D map where similar cells cluster together. This allows researchers to quickly identify different immune cell populations and see how they change in response to a disease or treatment. It performs automated cell population identification and sample classification to diagnose conditions and understand immune responses to infections or vaccines. In autoimmune disease, AI analyzes immunofluorescence images and protein profiles to enable earlier diagnosis and predict treatment responses.
These applications showcase the power of combining AI with comprehensive health data. At Lifebit, our platform is built to enable secure, federated analysis across global datasets, ensuring insights from millions of patients can inform individual care while protecting data.
The Problems Ahead: Overcoming AI’s Ethical and Practical Challenges

Despite its promise, AI in personalized medicine faces significant ethical and practical challenges that could deepen healthcare inequalities if not addressed.
Key ethical concerns include:
- Data Privacy: The use of sensitive genomic and health data requires robust security frameworks and strict adherence to regulations like GDPR and HIPAA to maintain trust.
- Algorithm Transparency: Many AI models operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult for clinicians and patients to understand their recommendations. The field of Explainable AI (XAI) aims to solve this by creating models that can justify their predictions. Techniques like SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) can highlight exactly which features—such as a specific genetic marker or lab result—contributed most to a particular recommendation. This transparency is crucial for building clinician trust and allowing for critical human oversight.
- Algorithmic Bias: AI trained on unrepresentative data can perpetuate or worsen healthcare disparities. For instance, if an AI algorithm designed to detect skin cancer is trained predominantly on images of light-skinned individuals, it may perform poorly at identifying malignant melanomas on darker skin, potentially leading to missed diagnoses and worse outcomes for patients of color. Continuous monitoring, fairness audits, and a concerted effort to build more diverse and representative datasets are essential to mitigate this risk.
- Healthcare Disparity: The high cost of AI adoption threatens to create a two-tier system where personalized medicine is only available to the wealthy.
Addressing implementation and validation challenges
Practical roadblocks also stand in the way of widespread adoption.
- Data Quality and Management: Real-world health records are often messy, inconsistent, and stored in disparate formats. Cleaning, standardizing, and managing this data, along with massive genomic files, requires significant investment in data infrastructure and governance.
- EHR Integration and Interoperability: AI tools must integrate seamlessly into clinical workflows to be effective. This requires not only technical integration with Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems but also solving the challenge of interoperability—ensuring data can be exchanged and understood across different systems using standards like FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources).
- Clinician Trust and Education: Doctors need training to understand AI’s capabilities and limitations. They must see clear evidence of its benefits through user-friendly interfaces that assist, not replace, their judgment.
- Cost, Validation, and Regulation: Implementation costs can be prohibitive for smaller institutions. Furthermore, all AI systems require rigorous clinical testing and continuous validation to ensure they are safe and effective. They also face regulatory hurdles from bodies like the FDA, which must develop new frameworks for approving adaptive algorithms that evolve over time.
The path forward through collaboration
No single group can solve these problems alone. Advancing AI in personalized medicine responsibly requires collaboration between technologists, physicians, academic researchers, and regulators.
- Technologists must build transparent and fair AI systems.
- Physicians must guide development and validate clinical utility.
- Researchers must rigorously evaluate outcomes and report findings honestly.
- Regulators must provide clear frameworks that protect patients without stifling innovation.
This collaborative ecosystem is the only path forward. At Lifebit, our federated AI platform is designed to enable secure, compliant collaboration. Our Trusted Research Environment allows diverse stakeholders to work together across data ecosystems without compromising security or privacy, building the foundation of governance and trust needed to realize AI’s full potential.
Frequently Asked Questions about AI in Personalized Medicine
How does AI actually personalize a treatment plan?
Traditional medicine often relies on a one-size-fits-all approach. AI in personalized medicine changes this by analyzing your unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and medical history to predict how your body will respond to specific treatments. For example, AI can identify a genetic variant that affects how you metabolize a heart medication and recommend a precise dosage to maximize benefits and minimize side effects. By synthesizing data from genomics, wearables, and clinical records, AI creates a health strategy designed for you, not a population average, enabling proactive and predictive care.
What is the difference between personalized medicine and precision medicine?
While often used interchangeably, there is a subtle distinction. Precision medicine is a broad term for treating patients based on the specific characteristics of their disease, such as the genetic profile of a tumor. It’s about finding the right treatment for the right patient. Personalized medicine is an even more comprehensive concept that considers not just the disease but the whole person—including their genetics, environment, lifestyle, and preferences—to create a truly individualized care plan. AI in personalized medicine is the key enabling technology for this holistic approach, as it can integrate all these different data types into a single, actionable strategy.
Is my health data safe when used by AI systems?
Yes, when the right security measures are in place. Protecting sensitive health information is paramount. Advanced techniques like federated learning allow AI models to analyze data without it ever leaving its secure location. The model “visits” the data to learn, but the raw data itself never moves or is exposed. This approach, combined with data encryption and strict governance within Trusted Research Environments (TREs), ensures that analysis complies with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. Security is the foundation of trustworthy AI in healthcare.
Will AI replace doctors in personalized medicine?
No. AI in personalized medicine is a tool to empower doctors, not replace them. AI excels at processing vast, complex datasets to find patterns and generate insights that would be impossible for humans to uncover alone. It acts as a powerful decision support tool, analyzing genomic, clinical, and real-time health data to provide doctors with relevant information. However, AI lacks the empathy, nuanced understanding, and clinical judgment that come from human experience. It frees clinicians from data-crunching to focus on what they do best: providing expert, compassionate care to their patients.
Is AI-driven personalized medicine affordable?
The cost of AI-driven personalized medicine is a significant concern, and initial applications, particularly those involving whole-genome sequencing, can be expensive. However, costs are rapidly decreasing. The price of sequencing a human genome has fallen from millions of dollars to a few hundred, making it far more accessible. Moreover, the long-term economic argument is compelling. By preventing chronic diseases, avoiding adverse drug reactions (which are a major cost to healthcare systems), and ensuring patients receive effective treatments from the start, personalized medicine has the potential to be highly cost-effective, shifting healthcare spending from reactive treatment to proactive prevention.
Conclusion: The Future is Personal, Powered by AI
We are in the midst of a healthcare revolution where your unique biology, not population averages, dictates your care. AI in personalized medicine has made this a reality. From decoding DNA for pharmacogenomics to creating “digital twins” from integrated health data, AI is enabling truly predictive and personalized healthcare.
However, this progress comes with challenges. We must steer the ethical complexities of data privacy, algorithmic bias, and transparency, as well as the practical problems of data quality, system integration, and cost. Overcoming these issues requires a collaborative ecosystem of technologists, clinicians, researchers, and regulators working toward a common goal.
At Lifebit, we are building the infrastructure for this future. Our next-generation federated AI platform provides secure, real-time access to global biomedical data, enabling large-scale, compliant research for biopharma, governments, and public health agencies. Through our Trusted Research Environment (TRE) and other solutions, we deliver the tools for advanced AI/ML analytics and federated governance. This allows sensitive health data to be analyzed without ever leaving its secure location, turning the complexity of global health data into actionable, personalized insights.
The future of healthcare is personal, predictive, and preventive. It is powered by AI, guided by human expertise, and grounded in ethical responsibility. That future is arriving now.
Learn more about our federated AI platform and find out how we’re making precision medicine a reality for patients worldwide.

