The Executive Guide to Trusted Data Foundations

Trusted Data Fabric: Stop Wasting AI Spend on Untrusted Data
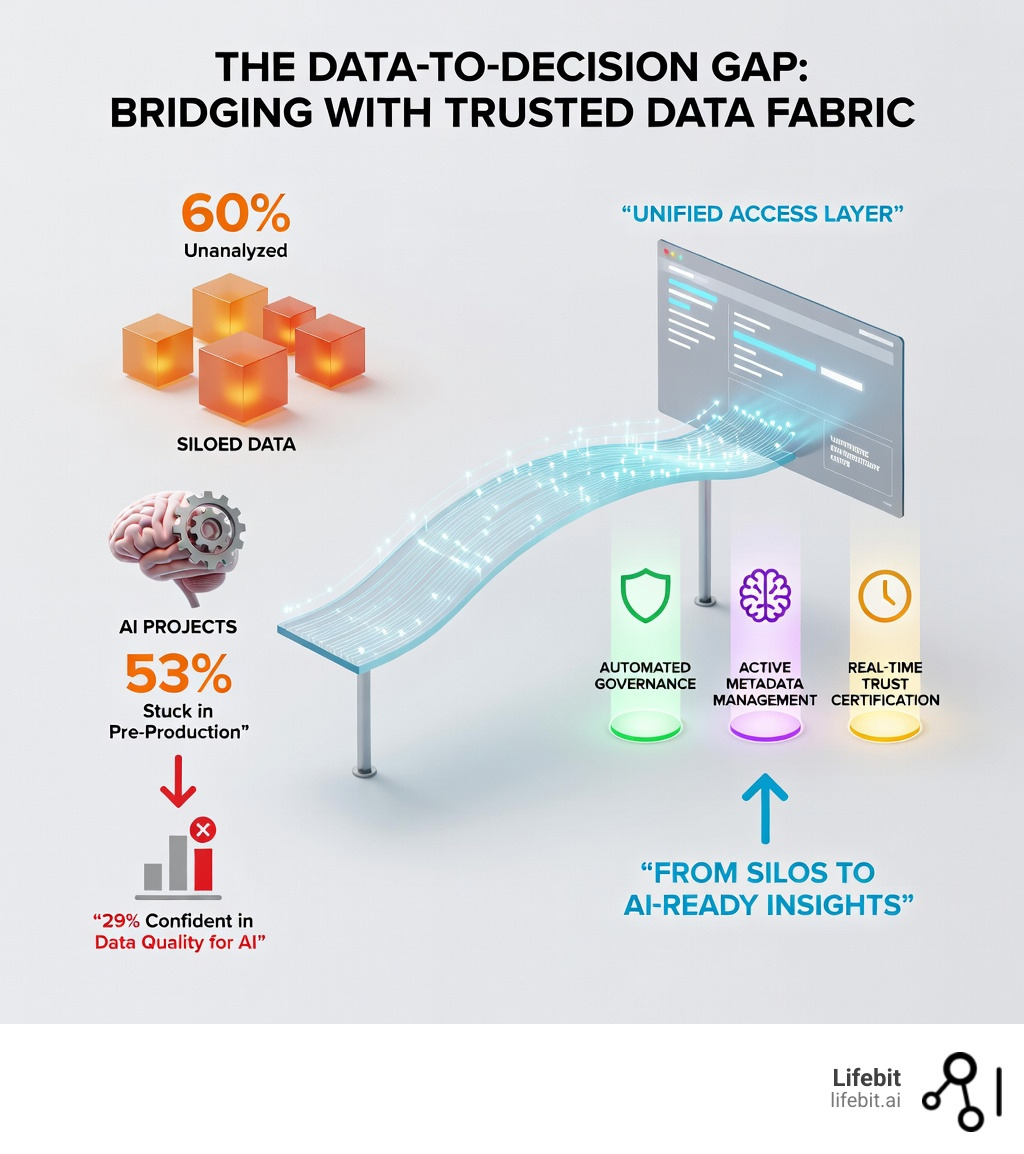
Trusted data fabric is an architecture that unifies data across disparate systems using metadata-driven automation, embedded governance, and real-time access controls—enabling organizations to turn siloed, unanalyzed data into AI-ready, compliant insights without physically moving data.
Key characteristics of a trusted data fabric:
- Unified access layer — Connects data across cloud, on-premises, and edge environments through virtualization
- Active metadata management — Uses ML to automatically find, catalog, and enrich data with business context
- Built-in governance — Applies policies as code across all data touchpoints for automated compliance (GDPR, HIPAA)
- Real-time processing — Enables self-service analytics and AI workflows on live data
- Trust certification — Monitors data quality, lineage, and provenance for explainable, auditable AI
For global pharma, public sector, and regulatory organizations, the data problem is clear: 60% of enterprise data remains unanalyzed, sitting in isolated EHR systems, claims databases, and genomics repositories. Meanwhile, only 29% of tech leaders believe their data has the quality, accessibility, and security needed to scale generative AI. The result? Slow cohort building, unreliable models, and regulatory bottlenecks that delay critical health decisions.
Legacy data warehouses and lakes were built for storage, not trust. They lack the metadata intelligence to track lineage, enforce governance automatically, or deliver real-time insights across federated environments. As data volumes explode—IDC predicts the global datasphere will reach 221 zettabytes by 2026—and AI regulations tighten, organizations need a new foundation: one that doesn’t just store data, but certifies it.
A trusted data fabric is that foundation. It uses metadata as connective tissue to weave together disparate sources into a single logical layer—without moving data. It automates governance, applies privacy controls by default, and enables self-service access for everyone from no-code analysts to high-code researchers. Most importantly, it builds trust into every layer: from data provenance tracking to real-time quality monitoring to AI-safe access controls.
I’m Dr. Maria Chatzou Dunford, CEO and Co-founder of Lifebit, where we’ve built a trusted data fabric for genomics and biomedical research that powers federated analytics across 275M+ patient records without data movement. My background in computational biology, AI, and health-tech entrepreneurship has shown me how the right data architecture—one that prioritizes trust, governance, and real-time access—unlocks breakthrough insights while protecting patient privacy and regulatory compliance.
Basic Trusted data fabric vocab:
Generative AI promises a revolution, but for most enterprises, the reality is sobering. 60% of enterprise data remains unanalyzed, often becoming “dark data” that is effectively invisible to decision-makers. This isn’t just a storage problem; it’s an architecture problem. Traditional data silos—where HR, supply chain, and clinical research data live in isolated boxes—prevent the cross-functional unification required for modern intelligence.
When data is scattered across hybrid environments, tech leaders struggle. While 67% of CFOs believe their teams have the data to capitalize on new tech, only 29% of tech leaders agree that their data has the necessary quality and security to scale AI. This “data-readiness gap” is why 53% of AI and ML projects are stuck in pre-production. Without a reliable way to access and trust the underlying information, AI models are built on shaky ground.
What Makes a Trusted Data Fabric Different
A traditional data fabric focuses on unification and connectivity. It’s a scalable solution that supports a combination of different integration styles. However, a trusted data fabric goes a step further by embedding “trust” as a core architectural component.
While a standard fabric might show you where the data is, a trusted fabric tells you why you should trust it. It offers:
- Versatility: The ability to handle structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data across across on-premises and multi-cloud environments.
- Scalability: As the global datasphere is projected to grow to 221 zettabytes by 2026, the fabric scales without requiring massive data migrations.
- Seamless Unification: It creates a single-entry point for consumers, making data unification a reality rather than a pipe dream.
Why Trust Is the Missing Link for Generative AI
If you’re building AI models for healthcare or finance, “good enough” data isn’t enough. Trust is the essential ingredient for Data Analysis Trusted Research Environments. To move models into production, we must ensure fairness, explainability, and privacy.
A trusted data fabric enables good flexibility for AI projects, reducing data preparation time and allowing models to learn more efficiently. By implementing bias guardrails and access policies directly into the fabric, we can mitigate risks before the first line of code is even written.
Core Components of a Trusted Data Fabric Architecture
Building a trusted data fabric isn’t about buying one single tool; it’s about assembling a sophisticated toolset that works in harmony. According to Forrester, there are six common layers that define a robust fabric architecture: data management, ingestion, processing, orchestration, discovery, and access. Each layer must be infused with trust-verification mechanisms to ensure the integrity of the output.

At its heart, the fabric relies on services and architectures that deliver reliable capabilities across environments. This includes virtualization, which allows us to query data where it lives, and Knowledge Graphs, which help AI interpret patterns and align them with business meaning.
Deep Dive: The Six Layers of Fabric Architecture
- Data Management Layer: This is the foundation where data governance and security policies are defined. In a trusted fabric, this layer acts as the ‘source of truth’ for policy enforcement, ensuring that data remains compliant with global regulations from the moment it is identified.
- Ingestion Layer: Unlike traditional ETL, the ingestion layer in a data fabric is often virtualized. It uses connectors to find and fetch data from diverse sources—SaaS apps, legacy databases, and IoT sensors—without requiring a physical move to a central repository.
- Processing Layer: This layer handles the transformation and cleaning of data. In a trusted environment, processing includes automated quality checks. If a data stream falls below a certain ‘trust score,’ the processing layer can flag it for manual review before it reaches an AI model.
- Orchestration Layer: This is the workflow engine. It coordinates the movement and transformation of data across the fabric, ensuring that the right data reaches the right consumer at the right time, following the most efficient path possible.
- Discovery Layer: Powered by active metadata, this layer allows users to find the data they need through a searchable catalog. It uses ML to suggest relevant datasets based on the user’s previous activity and role.
- Access Layer: The final interface where consumers—whether they are human analysts or autonomous AI agents—interact with the data. This layer enforces real-time access controls, ensuring that sensitive information is masked or encrypted based on the viewer’s permissions.
Metadata Management: The Brain of the Fabric
If the fabric is the body, metadata is the brain. It provides the context and understanding needed for the system to perform self-optimization. Through the intelligent use of metadata, a trusted data fabric can recognize new schema and automatically correct for “schema drift” without manual intervention.
By leveraging “active metadata,” the fabric doesn’t just store information about data—it uses it to cluster related data sets together and recommend the best integration paths. This is the foundation of Data Lakehouse Governance, ensuring that every user sees the data in a way that makes sense for their specific role. Active metadata also enables ‘self-healing’ data pipelines, where the system can identify a broken connection and automatically reroute the data flow based on historical patterns.
Data Trust Engineering and EMM 2.0
To truly certify a system, we look toward Data Trust Engineering + EMM 2.0. This framework shifts the focus from process-heavy governance to engineering-driven certification.
DTE certifies data systems based on use case, risk, and value, while EMM 2.0 manages metadata through modern graph technologies. Together, they provide Complete Data Trust Solutions that are vendor-neutral and AI-ready. This approach allows us to move beyond “box-ticking” compliance and into real-time trust monitoring, where the ‘trustworthiness’ of a dataset is calculated as a dynamic metric rather than a static attribute.
Building Governance and Security Into Your Data Fabric
In a trusted data fabric, security isn’t an afterthought—it’s woven into the thread. By combining virtualization with metadata management, the fabric expedites permission handling and automates security policies. This creates a ‘Zero Trust’ environment where every data request is verified, authorized, and encrypted, regardless of whether it originates inside or outside the network perimeter.
We advocate for “governance-as-code,” where policies are embedded directly into CI/CD pipelines. This ensures that every time a new data source is added or a model is updated, the system automatically checks against privacy and security standards. This is particularly vital for Building European Trusted Research Environments, where cross-border compliance is non-negotiable.
The Mechanics of Governance-as-Code
Implementing governance-as-code involves translating complex legal requirements into executable logic. For example, a GDPR requirement for ‘right to be forgotten’ can be coded into the fabric’s orchestration layer. When a deletion request is received, the fabric automatically identifies all instances of that user’s data across the federated network and executes the deletion or anonymization protocol without manual intervention.
Key benefits of this approach include:
- Consistency: Policies are applied identically across all environments, eliminating human error.
- Auditability: Every policy execution is logged, providing a clear trail for regulators.
- Agility: When regulations change (such as the introduction of the EU AI Act), developers can update the code in one place, and the change propagates across the entire fabric instantly.
Automating Compliance in a Trusted Data Fabric
Manual compliance checks are the enemy of speed. In a trusted data fabric, Advances in automatic policy enforcement mean that regulations like GDPR and HIPAA are applied at the point of access.
Whether you are using a Trusted Clinical Environment or a broader enterprise fabric, the system should automatically select the most appropriate encryption and masking techniques based on the user’s credentials and the sensitivity of the data. For instance, a researcher might see de-identified patient records, while a billing administrator sees only the financial fields necessary for their role, all pulling from the same underlying data source.
Data Provenance Standards for Transparent AI
Provenance matters. Just as we expect to know the source of our food or medicine, we must know the source of our data. Data provenance standards provide a blueprint for documenting the origin and lifecycle of data through 22 specific metadata fields, including the original collector, the date of acquisition, and any transformations applied.
Following these standards helps us build Trusted Data Collaboration frameworks. By tracking exactly how data was collected and modified, we create an audit trail that satisfies both internal auditors and external regulators. This transparency is the antidote to the ‘black box’ problem in AI, allowing organizations to explain exactly why a model made a specific prediction based on the lineage of the input data.
Trusted Data Fabric: Centralized Control, Real-Time Results
One of the biggest debates in data architecture is Data Fabric vs. Data Mesh. While a data mesh emphasizes decentralized domain ownership and treats data as a product, a trusted data fabric provides the overarching technical strategy and infrastructure that makes a mesh design viable. Think of the fabric as the high-speed rail system that allows different ‘cities’ (domains) to exchange Trusted Data Marketplace Guide products safely and efficiently.
| Feature | Traditional Data Management | Trusted Data Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Data Movement | Heavy ETL/ELT required | Minimal; uses virtualization |
| Governance | Manual/Siloed | Automated/As-Code |
| Metadata | Passive/Documentation only | Active/Drives automation |
| AI Readiness | Low (High prep time) | High (Self-service access) |
| Speed to Insight | Weeks/Months | Real-time/Hours |
| Architecture | Monolithic/Centralized | Federated/Logical Layer |
Why Centralized Data Fabric Delivers Faster, Safer AI
According to Gartner, real-time analytics and insights are among the top benefits of a data fabric. By providing a single logical layer, we enable immediate access to big data through metadata-driven capabilities. This centralized control doesn’t mean a bottleneck; it means a standardized “trust gate.”
This ‘trust gate’ is essential for scaling Generative AI. Without it, every data scientist must spend 80% of their time cleaning and verifying data. With a trusted fabric, the data is ‘pre-certified.’ The semantic layer ensures that when an AI model asks for ‘revenue,’ it receives a consistent definition across the entire enterprise, regardless of whether the data came from an Oracle database in London or a Snowflake instance in New York.
The Role of the Semantic Layer
A critical component of this centralized control is the Semantic Layer. This layer maps complex technical data structures to business concepts that humans and AI can understand. It acts as a translator, ensuring that the ‘language’ of the business is consistently applied. In a trusted data fabric, the semantic layer is dynamic; it evolves as the business evolves, ensuring that AI models don’t become obsolete as soon as a business process changes.
Real-World Impact: Turn Dark Data Into Real-Time Insights
When implemented correctly, a trusted data fabric drives innovative outcomes across every industry. For example, Sainsbury, a retail marketplace, leveraged a fabric to power over 30 custom analytics applications, helping store-floor staff make decisions in real-time regarding inventory and customer preferences. Similarly, Syracuse needed a unified platform to connect private and public cloud data centers, which the fabric provided seamlessly, reducing data latency by 40%.
Industry-Specific Use Cases
- Financial Services: Large banks use trusted data fabrics to combat fraud in real-time. By weaving together transaction data from legacy mainframes with real-time mobile app logs, the fabric allows AI models to detect suspicious patterns across the entire customer journey, reducing false positives and protecting assets.
- Manufacturing and IoT: In the ‘Industry 4.0’ era, factories generate terabytes of sensor data. A trusted data fabric connects these edge devices to central predictive maintenance models. This allows manufacturers to predict equipment failure before it happens, saving millions in downtime while ensuring that sensitive proprietary designs remain secure within the local environment.
- Healthcare and Life Sciences: This is where the impact is most profound. Lifebit’s own Federated Trusted Research Environment allows researchers to gain efficient insights from The Internet of Things (IoT) and clinical datasets while minimizing latency and maximizing privacy. By enabling federated analytics, researchers can run queries across global biobanks without the data ever leaving its secure home.
Measuring the ROI of a Trusted Data Fabric
Organizations looking to justify the investment in a data fabric should focus on three key metrics:
- Time-to-Insight: How long does it take from a business question being asked to an answer being delivered? Fabrics typically reduce this from weeks to hours.
- Data Engineering Efficiency: By automating 70% of data integration tasks through active metadata, organizations can redirect their most expensive talent toward high-value AI development.
- Risk Mitigation: The cost of a single data breach or regulatory fine can be catastrophic. A trusted fabric provides a quantifiable ‘security posture’ that reduces the likelihood of compliance failures.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
We won’t pretend it’s easy. Building a trusted data fabric involves navigating system complexity and securing stakeholder buy-in. Common problems include:
- Legacy Integration: Connecting to decades-old systems that weren’t designed for APIs.
- Control Concerns: Convincing domain owners that centralized governance doesn’t mean losing autonomy over their data.
- Skill Gaps: The need for teams that understand Data Trust Engineering and graph-based metadata management.
To overcome these, we recommend starting with a Trusted Research Environment Complete Guide approach: identify a high-value use case (like a specific AI pilot), demonstrate the ROI of trusted access, and then scale the fabric across the organization incrementally.
Frequently Asked Questions About Trusted Data Fabric
How Is a Trusted Data Fabric Different From Traditional Data Management?
Traditional management relies on moving data into central lakes or warehouses, often losing context and trust along the way. A trusted data fabric uses virtualization and active metadata to provide a unified view without moving the data, while Data Trust Engineering ensures every byte is certified for its specific use case.
What Are the Top Trusted Data Fabric Capabilities for 2025?
Modern trusted data fabric solutions now offer:
- Automated Lineage: Seeing exactly how data evolved.
- Semantic Modeling: Preserving business context across the entire data ecosystem.
- Real-time Event Streaming: Integrating live data flows for immediate analysis.
- Knowledge Graphs: Modeling complex relationships to power explainable AI.
How Can Organizations Assess Their Readiness for Trusted Data Fabric?
Start by looking at your “dark data” percentage. If more than 50% of your data is unanalyzed, you’re ready for a fabric. Assess your current multi-cloud support and determine if your governance is manual or automated. If you’re struggling to gain traction with AI projects, the lack of a trusted foundation is likely the culprit.
Conclusion: Build Your AI-Ready Data Foundation With Lifebit
At Lifebit, we believe that the future of medicine and enterprise intelligence depends on trust. Our Lifebit Federated Biomedical Data Platform is designed to be the ultimate trusted data fabric for the most sensitive data on earth.
By integrating our Trusted Research Environment (TRE) with our Trusted Data Lakehouse, we provide the Real-time Evidence & Analytics Layer (R.E.A.L.) needed to turn global data into life-saving insights. Don’t let your data stay dark. Build a foundation that is secure, federated, and—above all—trusted.

