Beyond Centralized AI: Exploring the Power of Distributed Architectures

Why Organizations Are Moving Beyond Centralized AI
A Distributed AI platform runs AI workloads across interconnected nodes—edge devices, on-premise servers, or cloud clusters—rather than a single data center. This allows organizations to process data locally, maintain data sovereignty, and scale AI without moving massive datasets.
Key characteristics of a Distributed AI platform:
- Decentralized processing: AI models run across multiple nodes instead of a single server
- Data stays local: No need to aggregate sensitive data in one place
- Collaborative learning: Nodes share insights without sharing raw data (e.g., federated learning)
- Fault tolerance: System continues functioning even if individual nodes fail
- Lower latency: Real-time inference happens close to data sources and users
Traditional centralized AI faces significant challenges: data silos, privacy risks under regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, and struggles with scalability for petabyte-scale data and low-latency for real-time applications like pharmacovigilance.
Distributed AI solves these problems by bringing computation to the data. It uses a network of intelligent nodes where each node processes data locally and shares insights, not raw data, to build a collective intelligence. This paradigm shift is changing drug findy, public health monitoring, and real-world evidence analysis—all while keeping data secure, compliant, and under institutional control.
The numbers tell the story. According to Gartner, AI trust, risk, and security management is the #1 strategic trend in 2024. By 2026, organizations that operationalize AI transparency, trust, and security will see a 50% increase in adoption, business goals, and user acceptance. Meanwhile, 84% of organizations already have moderate to high generative AI adoption, with 41% using open-source infrastructure to power it.
I’m Maria Chatzou Dunford, CEO and Co-founder of Lifebit, where we’ve built a Distributed AI platform specifically for genomic and biomedical data that enables federated analytics across siloed datasets. Over 15 years working in computational biology, AI, and health-tech, I’ve seen how distributed architectures open up insights that centralized systems simply can’t access.
Handy Distributed AI platform terms:
What is Distributed AI and How Does It Differ from Centralized AI?
Distributed AI represents a fundamental shift in AI design and management. Instead of concentrating computing power and data centrally, a Distributed AI platform spreads tasks across interconnected nodes, enabling collaborative learning and problem-solving among distributed AI agents.
A distributed system works by distributing tasks across multiple nodes for collaboration and parallel processing. This improves reliability, performance, and scalability. It is less like a single, central brain and more like a network of brains working together.
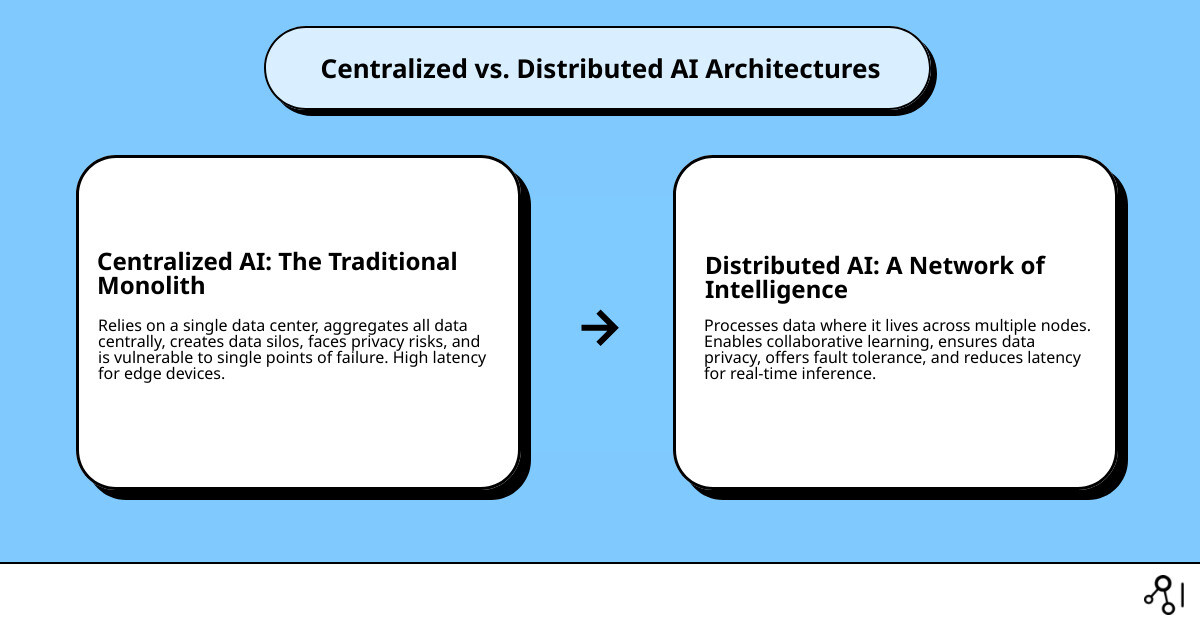
Centralized AI: The Traditional Monolith
Centralized AI, the traditional standard, collects all data in a single data center or cloud server for model training and deployment. While simple for small-scale use, it has significant drawbacks:
- Data Gravity: Moving massive datasets is slow, costly, and creates latency.
- Vulnerability: A single point of failure can bring down the entire system.
- Scalability Bottlenecks: Scaling requires costly upgrades to a single machine, which has physical limits.
- Privacy Concerns: Centralizing sensitive data creates a security risk and complicates compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. For teams working with biomedical and multi-omic data, this is a non-starter.
- High Latency for Edge Devices: Processing data far from its source causes delays, making it unsuitable for real-time applications.
Distributed AI: A Network of Intelligence
In contrast, a Distributed AI platform accepts decentralization. It distributes computational tasks across various nodes—from edge devices to on-premise servers or cloud clusters. These nodes work in parallel, sharing resources to solve problems collaboratively.
The key differences are profound:
- Task Distribution: Tasks are spread across multiple nodes for parallel processing and faster results.
- Improved Reliability: With no single point of failure, the system remains operational even if some nodes go offline (fault tolerance).
- Improved Scalability: New nodes can be added to the network to scale horizontally and cost-effectively as needs grow.
- Data Locality: Data is processed near its source, reducing latency and addressing data sovereignty concerns. This is crucial for sensitive patient data in regions like the UK, USA, Canada, Israel, Singapore, and across Europe.
- Resource Sharing: Nodes share computational resources, leading to more efficient use and lower operational costs.
This paradigm shift moves organizations away from the traditional monolith to a dynamic, resilient network of intelligent agents.
The Unmissable Advantages of a Distributed AI Architecture
Adopting a Distributed AI platform yields tangible improvements in performance, cost, security, and trust. It offers significant benefits over traditional approaches, helping organizations in biopharma, government, and public health accelerate their AI advantage.
Boosting Security, Trust, and Adoption
In today’s landscape, trust, risk, and security management for AI is paramount. Gartner highlights this as a top strategic trend, predicting that by 2026, organizations that operationalize AI transparency and security will see a 50% increase in adoption and business success. Embracing robust security is a direct driver of success.
- Data Privacy and Sovereignty: A compelling advantage, especially in biomedical research, is keeping sensitive data local. A modern distributed platform ensures patient data remains within its originating institution or country (e.g., UK, USA, Canada, Israel, Singapore, or European nations), adhering to strict privacy regulations. This reduces data breach risks and enables compliance without compromising research.
- Reduced Risk: By processing data on-premise or at the edge, organizations minimize the need to transfer sensitive information across networks, lowering exposure to cyber threats. This defense-in-depth approach to securing AI is crucial.
- Improved Trust: When data owners know their data stays local and is processed under their control, it builds trust, fostering collaboration on larger, more diverse datasets. This is essential for federated analytics across global biomedical datasets.
Achieving Unprecedented Scale and Efficiency
Distributed AI is also about opening up new levels of performance and cost-effectiveness.
- Improved Scalability: A Distributed AI platform naturally scales horizontally. As data grows or computational demands increase, new nodes can be added to the network. This allows organizations to handle massive datasets and complex AI models that would overwhelm a single centralized system.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: By distributing workloads, teams can make better use of available computing resources. This often means leveraging existing infrastructure more effectively, rather than investing in ever-larger supercomputers. For instance, modern frameworks for agentic AI systems allow thousands of agents to run on-demand on minimal hardware with very low latency, demonstrating significant efficiency gains.
- Lower Latency and Real-time Inference: Processing data closer to the source (at the edge) dramatically reduces latency. This is critical for applications requiring immediate insights, such as real-time patient monitoring or rapid safety signal detection in pharmacovigilance.
- Cost-Effective AI Adoption: By optimizing infrastructure and minimizing data transfer, distributed architectures can lead to significant cost savings. The ability to scale to zero for certain workloads, a feature of some advanced agent models, means organizations only pay for compute when it is actively used, eliminating unnecessary expenses.
For Lifebit clients, these advantages are realized through a federated AI platform that integrates Trusted Research Environments, Trusted Data Lakehouses, and real-time analytics layers to deliver secure, scalable insights on sensitive biomedical and multi-omic data.
Core Components of a Modern Distributed AI Platform
Building a robust Distributed AI platform requires careful consideration of several key components and architectural considerations. It is about creating a flexible, resilient ecosystem where AI workloads can thrive across diverse environments while respecting data sovereignty and regulatory constraints.

Architectural Building Blocks
A modern Distributed AI platform is typically built upon a flexible architecture that scales from edge devices to cloud clusters. This is often described in terms of a three-tier model: Edge, Node, Core.
- Edge Devices: These are the closest to the data source, performing initial processing and inference with minimal latency. They could be sensors, IoT devices, or local servers in a hospital.
- Nodes: These represent larger compute units, such as on-premise servers or regional data centers. They handle more complex tasks, aggregate data from edge devices, and participate in distributed training.
- Core: This could be a central cloud environment or a large data lakehouse, providing extensive storage, advanced analytics, and global model aggregation.
Key architectural elements include:
- Communication Middleware: This layer facilitates seamless interaction between distributed components. Protocols and frameworks for efficient data exchange and coordination are vital. For instance, some platforms use advanced interconnects for a dramatic reduction in latency between devices.
- Orchestration Engine: This manages the deployment, scaling, and lifecycle of AI models and agents across the distributed network. Modern orchestration engines, such as the Exosphere reliability runtime, provide a reliability layer for AI agents, offering inbuilt failure handling and dynamic execution graphs for robust workflow orchestration.
- Data Governance and Management: Ensuring data quality, lineage, and access control across distributed datasets is paramount. Federated governance models address this by providing secure, compliant access to biomedical and multi-omic data without centralizing it.
- State Persistence: In distributed systems, maintaining the state of ongoing processes and models is crucial for resilience. Native state persistence is a key feature, ensuring workflow state is preserved across restarts and failures.
- Observability Dashboards: Monitoring the performance, health, and activity of distributed AI components is essential. Tools for visual monitoring, debugging, and real-time execution tracking help teams keep tabs on complex systems.
Types of Distributed Learning
Distributed learning is the engine that powers a Distributed AI platform, enabling models to be trained and improved across various locations without necessarily centralizing raw data. This approach encompasses several distinct methods, as described in What is Distributed Learning?:
| Type of Distributed Learning | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Federated Learning | Models are trained across decentralized devices or servers holding local data samples, without exchanging them | Preserves data privacy while enabling collaborative learning |
| Ensemble Learning | Multiple models are trained independently and their predictions are combined | Improves accuracy and reduces overfitting |
| Collaborative Learning | Multiple agents or models work together, sharing knowledge and insights | Enables complex problem-solving through collective intelligence |
| Data Parallelism | Training data is split across multiple nodes, each processing a subset | Accelerates training on large datasets |
| Model Parallelism | Different parts of a model are distributed across multiple devices | Enables training of models too large for a single device |
Distributed AI in Action: From Autonomous Cars to Genomic Research
The power of a Distributed AI platform is not just theoretical; it is changing industries across the globe, from our daily commutes to life-saving medical breakthroughs. By bringing AI computation closer to where data is generated and consumed, organizations can open up applications that centralized systems simply cannot handle due to latency, privacy, or scale.
Revolutionizing Healthcare and Biomedical Research
In healthcare and biomedical research, the impact of Distributed AI is profound. It enables a future where AI-driven drug findy is accelerated, pharmacovigilance is proactive, and personalized medicine becomes a reality, all while safeguarding patient privacy.
- Federated Analytics on Sensitive Data: One of the most critical applications is enabling federated analytics on sensitive patient data. Researchers across multiple hospitals in London, New York, Singapore, Tel Aviv, Toronto, or European research hubs can collaborate on a study without ever centralizing raw patient records. Platforms like Lifebit’s make this possible, allowing AI models to learn from diverse datasets while data remains securely within its institution. This is vital for compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, which are strictly enforced in Lifebit’s operating regions.
- AI-Driven Drug Findy: By leveraging distributed AI, it becomes possible to analyze vast, multi-omic datasets (like genomic, proteomic, and clinical data) spread across different research centers. This accelerates the identification of novel drug targets and the development of new therapies. Biotech innovators are using distributed AI platforms to speed up findy and reduce R&D costs.
- Real-time Insights and Safety Surveillance: In pharmacovigilance, the ability to rapidly detect safety signals from real-world evidence is paramount. A Distributed AI platform can process incoming data streams from various sources in real time, enabling faster detection of adverse events and improving patient safety.
- Genomic Data Analysis: Analyzing the massive scale of genomic data demands distributed computing. Lifebit’s federated platform excels here, providing secure, real-time access to global biomedical and multi-omic data, with built-in capabilities for harmonization and advanced AI/ML analytics through components like its Trusted Research Environment and Trusted Data Lakehouse.
Beyond healthcare, distributed AI is driving progress in other critical areas:
- Autonomous Vehicles: These rely on a distributed network of sensors and processors to interpret and respond to dynamic environments. Each vehicle contributes to the collective intelligence of the system, enabling real-time decision-making for navigation and safety.
- Smart Grids: Distributed AI optimizes energy distribution, predicts demand, and manages renewable energy sources across vast networks, improving efficiency and reliability.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): In manufacturing, distributed AI enables real-time quality control and predictive maintenance by deploying AI nodes on the factory floor. This allows for on-premise processing of sensitive operational data, ensuring data sovereignty and reducing downtime.
- Radio Access Networks (RANs): Existing approaches to AI adoption in RANs are often inadequate for realizing truly AI-native 6G networks. A distributed AI platform architecture is being proposed as a solution to address the practical challenges hindering widespread AI adoption in the RAN space, paving the way for more intelligent and efficient communication networks.
- Recommendation Systems: Platforms such as global streaming or e-commerce services use reinforcement learning within a distributed framework to provide personalized recommendations, learning from user interactions across many devices.
Powering Enterprise and Generative AI
The enterprise world is rapidly embracing AI, with distributed architectures playing a crucial role.
- High Generative AI Adoption: The numbers speak for themselves: 84% of organizations currently have moderate to high generative AI adoption. A significant portion, 41%, are using open-source infrastructure for their Generative AI initiatives. This highlights a clear trend towards flexible, adaptable, and often distributed solutions.
- AI Agent Systems: Modern frameworks are designed to build production-grade, resilient AI agent systems that operate at scale. These agents can reason, act, and collaborate across distributed compute environments, integrating with numerous enterprise data sources. This enables complex, multi-step workflows in areas like customer service, data analysis, and automated decision-making.
- Resilient Workflows: Enterprise AI often involves mission-critical processes. A Distributed AI platform, with its inherent fault tolerance and robust workflow orchestration, ensures that these AI-driven operations continue uninterrupted, even in the face of network issues or node failures. For Lifebit clients in biopharma and public health, this level of reliability is essential, as downtime can have severe consequences.
For more on how federated platforms support these use cases, see More info about federated platforms.
How to Implement and Manage a Distributed AI Ecosystem
Implementing and managing a Distributed AI platform effectively is a strategic undertaking that requires careful planning, the right tools, and a strong focus on governance and security. It is about building an intelligent, interconnected ecosystem that spans edge, on-premise, and cloud environments while honoring data sovereignty.
Building a Scalable Distributed AI Platform
The journey to a scalable distributed AI ecosystem begins with strategic planning and selecting the right technological foundation.
- Choosing the Right Framework: There are numerous open-source frameworks and tools designed to facilitate distributed AI. Some, like DLRover, make the distributed training of large AI models easier and more efficient, while others, such as Kedro, help create reproducible and maintainable data science code.
- Infrastructure Selection: Whether deploying on edge devices, on-premise servers, or cloud clusters, the underlying infrastructure must support the distributed nature of the AI workloads. Some solutions provide purpose-built high-performance data centers and edge-to-cloud connectivity for low latency.
- Automatic Device Findy and Parallelism: Platforms designed for distributed AI often include features like automatic device findy, where devices can find each other without manual configuration. Furthermore, topology-aware auto-parallelism helps to optimize model splitting and distribution based on device resources and network conditions, ensuring efficient use of compute power. For example, some platforms leverage tensor parallelism to achieve significant speedups.
- MLOps for Distributed Systems: Operationalizing AI models in a distributed environment requires robust MLOps practices. This includes continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) for models, automated monitoring, and version control across distributed nodes. The LF AI & Data Foundation actively promotes open-source innovation in AI and data, fostering collaboration and providing trusted infrastructure to support these efforts.
Managing a Secure Distributed AI Platform
Security and governance are non-negotiable when dealing with distributed AI, especially with sensitive biomedical and multi-omic data.
- Data Sovereignty Controls: A modern platform should be designed with federated governance, ensuring that data remains within its sovereign boundaries (for example in the UK, USA, Canada, Israel, Singapore, or specific European countries). This is achieved through strict access controls and processing data locally, minimizing cross-border data transfers.
- AI Security Frameworks: Organizations should adopt comprehensive AI security frameworks to protect models and data. A defense-in-depth approach is needed, cataloging AI security risks and offering actionable recommendations. This includes addressing issues like data breaches, regulatory non-compliance, and adversarial attacks on AI models.
- Resiliency Policies: A Distributed AI platform must be resilient. Modern frameworks allow platform teams to apply resiliency policies—including timeouts, retries, and circuit breakers—to the databases and message brokers used by AI agents. This ensures that workflows complete even in the face of transient failures.
- Access Control and Encryption: Implementing robust Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and end-to-end encryption is fundamental. Some frameworks provide built-in RBAC and use mTLS to encrypt communication layers, ensuring secure interactions between distributed components.
- Transparency and Trust: As a top strategic trend in 2024, AI trust and transparency are paramount. Ensuring that AI-driven decisions are auditable and explainable is crucial for adoption and regulatory approval in sensitive domains. The LF AI & Data Foundation also emphasizes open-source innovation to foster collaboration and transparency in AI.
Lifebit embeds these principles into its federated AI platform, combining secure infrastructure, real-time analytics, and strong governance to help organizations implement distributed AI ecosystems responsibly.
The Future is Distributed: Trends and Implications
The trajectory of AI is undeniably moving towards distributed architectures. We are witnessing a paradigm shift that will reshape industries and open up unprecedented capabilities, especially in sensitive data environments like biomedical research, public health, and regulated enterprise.
- Sovereign AI: The concept of “Sovereign AI” is gaining traction, where countries and organizations seek to build and control their own AI infrastructure and data, ensuring national security, economic independence, and data privacy. This aligns closely with the principles of a Distributed AI platform, allowing processing to happen within geographical and regulatory boundaries, as is critical for operations in the UK, USA, Israel, Singapore, Canada, and across Europe.
- AI-Native Networks (6G): The evolution of communication networks towards 6G is inherently linked to distributed AI. Future 6G networks are envisioned to be “AI-native,” meaning AI will be deeply embedded in their architecture and operations. This will require distributed AI platforms to manage and optimize complex network functions, addressing challenges in Radio Access Networks (RANs) and beyond.
- Hyper-Distributed AI: We are moving towards an era of “hyper-distributed AI,” where AI capabilities are pervasive, embedded in everything from tiny edge devices to vast cloud infrastructures. This means AI will be seamlessly integrated into our environments, providing intelligence where and when it is needed most, with minimal latency.
- Explainable AI (XAI): As AI systems become more complex and distributed, the need for transparency and interpretability grows. Explainable Reinforcement Learning (XRL) is crucial for ensuring transparency and interpretability in decision-making processes within distributed AI. This is particularly important in healthcare, where clear explanations for AI-driven decisions are vital for optimizing treatment plans and building clinician trust.
- The Rise of AI Agents: AI agent systems will become increasingly sophisticated, capable of reasoning, acting, and collaborating across distributed environments. These agents will automate complex tasks, integrate diverse data sources, and operate with high resilience and scalability, becoming indispensable in enterprise AI adoption.
- Increased Automation and Democratization of AI: As distributed AI platforms become more accessible, we will see greater automation of AI model deployment and management. This democratization of AI computation will allow smaller organizations, not just global enterprises, to run their own AI clusters, making powerful AI capabilities more widely available.
For Lifebit, these trends reinforce the importance of federated, privacy-preserving architectures that keep data local while enabling global-scale insights through secure collaboration.
Conclusion
We have journeyed through the landscape of Distributed AI, understanding its fundamental differences from traditional centralized approaches and uncovering its immense potential. A Distributed AI platform is more than just a technological advancement; it is a strategic imperative for organizations navigating the complexities of data privacy, regulatory compliance, and the demand for real-time, scalable AI solutions.
The benefits are clear: from improved scalability, improved fault tolerance, and efficient resource utilization to critical data privacy preservation and reduced latency, distributed architectures offer a powerful paradigm shift. We have seen how these platforms are revolutionizing fields from autonomous vehicles and industrial IoT to, most importantly for Lifebit, healthcare and biomedical research, enabling secure federated analytics on sensitive data and accelerating drug findy.
Lifebit’s federated AI platform is specifically engineered to bring computation to the data, ensuring that sensitive biomedical and multi-omic information remains secure within its sovereign boundaries in regions such as the UK, USA, Canada, Israel, Singapore, and across Europe, while still contributing to global scientific progress. By operationalizing AI transparency, trust, and security, Lifebit empowers organizations to achieve their business goals and drive significant adoption.
The future of AI is undeniably distributed. It is a future where AI is not confined to a single data center but woven into the fabric of our interconnected world, opening up new possibilities in sensitive domains and beyond. Lifebit is at the forefront of this change, building the infrastructure that allows researchers and clinicians to collaborate securely and derive life-changing insights from vast, siloed datasets.
Are you ready to open up the full potential of your data while maintaining complete control and compliance? Start your journey with federated data analysis and find how our Distributed AI platform can transform your research and operations.

