The Big Brother Upgrade with AI Powered Surveillance

Stop Security Breaches: How AI Powered Surveillance Detects Threats in Seconds
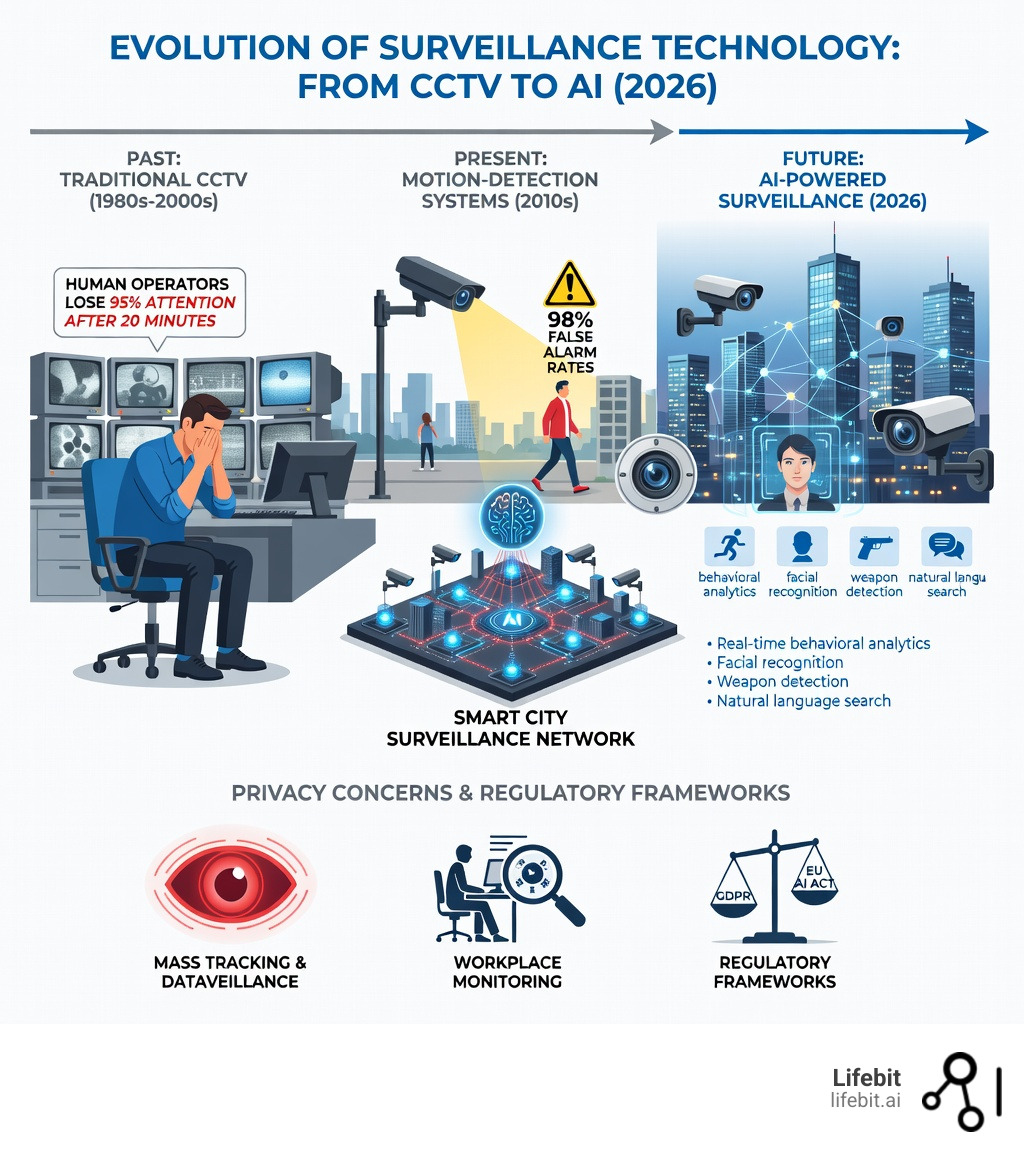
AI powered surveillance systems use machine learning algorithms to analyze video feeds in real-time, detecting objects, behaviors, and threats far beyond what human operators can monitor. Unlike traditional CCTV that relies on humans watching screens, AI surveillance continuously processes footage from thousands of cameras simultaneously—identifying weapons, tracking individuals through facial recognition, flagging unusual behavior, and alerting security teams to potential threats before they escalate.
Key capabilities of AI powered surveillance:
- Facial recognition and behavioral analytics – Identifies individuals and detects suspicious patterns in real-time
- Weapon and threat detection – Spots guns, knives, or concealed weapons using thermal imaging and object recognition
- Continuous monitoring without fatigue – Analyzes footage 24/7 with consistent accuracy (humans lose 95% attention after 20 minutes)
- Natural language search – Find specific events instantly by searching “person in red jacket” or “vehicle entering at 3pm”
- Proactive alerts and automated response – Triggers sirens, notifies police, or locks doors based on detected threats
Major concerns:
- Privacy erosion – Mass tracking, facial recognition databases, and dataveillance threaten individual autonomy
- Workplace monitoring – Employers track keystrokes, facial expressions, and productivity metrics often without disclosure
- False positives and bias – AI systems still struggle with accuracy in poor lighting, diverse populations, and crowded environments
- Regulatory gaps – Many regions lack comprehensive laws governing AI surveillance deployment
The technology isn’t coming—it’s already here. In China, AI surveillance integrates facial recognition with social media monitoring to track dissidents in real-time. In the U.S., the Department of Homeland Security uses AI to scan visa applicants’ social media for “extremist rhetoric.” Companies like Eagle Eye Networks have deployed cloud-based systems across more than 7,500 cameras, replacing the old “rewind and review” model with proactive, AI-driven threat detection.
But this change raises urgent questions about consent, transparency, and the balance between security and freedom. How much surveillance is too much? Who controls the data? And can we deploy these systems responsibly without sliding into mass tracking?
I’m Dr. Maria Chatzou Dunford, CEO and Co-founder of Lifebit, where we’ve spent over 15 years building federated AI platforms for secure biomedical data analysis. While AI powered surveillance in public spaces raises critical privacy concerns, the same technologies—when applied to healthcare data—can save lives through real-time pharmacovigilance and disease monitoring without compromising individual privacy. Let me walk you through how AI surveillance actually works, where it’s headed, and what we can do to ensure it serves humanity rather than controls it.
AI powered surveillance vocab to learn:
- data integrity in health information systems
- health data integration
- what is data integrity in health care
When we talk about AI powered surveillance, we aren’t just talking about a clearer picture. We are talking about a system that understands what it sees. Traditional CCTV is like a silent witness that only speaks when spoken to (usually after a crime has happened). Modern AI surveillance is more like a digital detective that never sleeps, never blinks, and has a photographic memory of everything it has ever seen.
At its core, these systems use machine vision algorithms to compare observed objects against millions of reference images. If a standard 1-megapixel camera is equipped with onboard video analytics, it can detect a human at a distance of about 350 feet even in non-ideal conditions. This isn’t just “motion detection”—which, let’s be honest, usually just alerts you to a stray cat or a blowing leaf. This is high-efficacy detection based on probability and pattern recognition.
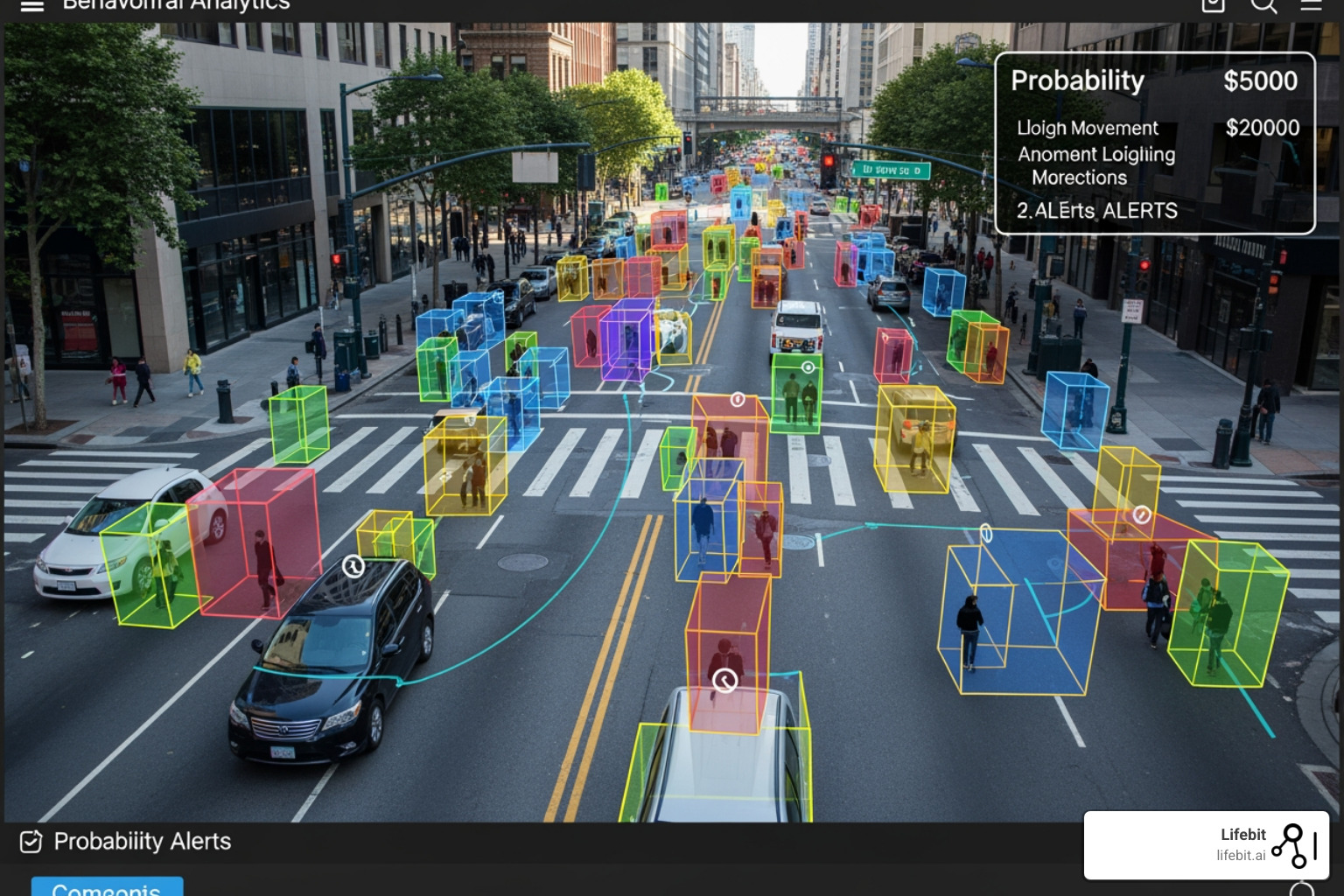
One of the most significant leaps is in behavioral analytics. Unlike rule-based systems that require a programmer to set “if-then” scenarios, behavioral AI is self-learning. It “normalizes” an environment—learning what a typical Tuesday afternoon looks like in a busy London terminal—and then flags the anomaly. A car driving onto a sidewalk or a person loitering in a restricted zone for exactly 47 seconds longer than average triggers an instant alert.
Research into video analytics for threat detection shows that using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) can even help these systems “fill in the blanks” when footage is grainy or obstructed, making them far more reliable than the “improve” button we see in Hollywood movies.
Real-Time Threat Detection and Crisis Prevention
The true value of AI powered surveillance lies in its ability to act before the “review and rewind” phase. Take gun detection, for instance. Systems today use a triple-layer verification process: the AI identifies the shape of a weapon, thermal imaging confirms a heat signature consistent with a firearm, and a human reviewer is instantly pinged to verify the threat. This happens in seconds, allowing for talk-down deterrence over loudspeakers or immediate lockdown procedures.
In drug safety, we use similar “real-time” logic. Just as a security system spots a weapon, our real-time pharmacovigilance tools spot adverse drug reactions (ADRs) across global datasets. The goal is the same: identify the threat before it becomes a catastrophe.
Public Health and Safety Monitoring
During the global health crises of the last few years, we saw AI powered surveillance move from the police station to the hospital and the construction site. Systems now monitor for PPE compliance—ensuring every worker on a Singapore site is wearing their helmet—and use environmental sensors to detect leaks or air quality issues.
In our work at Lifebit, we see the parallel in Real-time Adverse Drug Reaction Surveillance. By monitoring data patterns, we can identify public health risks long before they hit the evening news. It’s about being proactive rather than reactive, whether you’re protecting a building or a population.
Humans Miss 95% of Crimes: How AI Powered Surveillance Fixes It
We have to face a hard truth: humans are terrible at watching surveillance monitors. It’s not a lack of effort; it’s biology. Studies show that a human watching a single video monitor for more than twenty minutes loses 95% of their ability to maintain attention sufficient to discern significant events. If you give that same person two monitors, their attention loss is cut in half again—meaning they are effectively missing 97.5% of what’s happening.
Traditional CCTV is a “dumb” pipe. It records everything but understands nothing. This leads to a massive efficiency gap. Companies typically spend only about 4% of their actual security losses on preventative measures. They wait for the loss to happen, then spend a fortune trying to figure out who did it.
| Feature | Human Operator | AI Powered Surveillance |
|---|---|---|
| Attention Span | Drops 95% after 20 mins | 100% 24/7/365 |
| False Alarm Rate | High (over 98% for burglar alarms) | Low (Filtered by object recognition) |
| Search Speed | Hours/Days of manual review | Seconds via Natural Language |
| Scalability | Limited by headcount | Unlimited via Cloud/Edge |
| Response Time | Reactive (after event) | Proactive (real-time alerts) |
Solving the 98% False Alarm Problem with AI Powered Surveillance
If you’ve ever been woken up at 3 AM by a building alarm only to find out it was a moth, you know the “98% problem.” Over 98% of burglar alarms reported to police are false. This has led to “alarm fatigue” where police departments deprioritize these calls.
AI powered surveillance fixes this by adding a layer of intelligence. Instead of a simple tripwire, the system asks: “Is this a human? Is this a vehicle? Is this an authorized person?” By filtering out the noise, AI ensures that when an alert is sent, it’s worth acting on. This accuracy is exactly what we strive for in our AI for Pharmacovigilance Complete Guide, where we use AI to filter out “noise” in patient data to find true safety signals.
Natural Language Search and Rapid Investigation
The “needle in a haystack” problem is gone. With natural language search, investigators no longer scrub through 48 hours of footage. They type: “Red backpack and grey jacket” or “Blue truck entering parking lot B.” The system uses metadata tagging to pull up every time-stamped instance of that description in seconds. This speed doesn’t just catch criminals; it saves lives in emergency response scenarios where every second counts.
Stop Dataveillance: Use AI Powered Surveillance Without Violating Privacy
We wouldn’t be doing our jobs if we didn’t talk about the “Big Brother” in the room. The transition from surveillance to dataveillance is a significant ethical shift. Traditional surveillance watches a place; dataveillance tracks a person across their entire digital and physical life.
In China, we see the most extreme version of this: AI systems integrated with social media monitoring to identify dissidents. But the U.S. and Europe aren’t immune. Reports have surfaced about the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) analyzing social media posts to look for “extremist” rhetoric—a term that is notoriously difficult to define. When advanced AI meets abundant, non-secured data and data brokers, the risk of privacy, safety, and disinformation concerns skyrockets.
Navigating the Regulatory Landscape of AI Powered Surveillance
Regulations like the GDPR and the upcoming EU AI Act are trying to catch up. The goal is to balance the need for security with individual autonomy. For instance, the AI Act categorizes certain types of biometric surveillance as “high risk,” requiring strict transparency and human oversight.
At Lifebit, we believe that compliance isn’t a hurdle; it’s a foundation. Our Pharmacovigilance Compliance Solution is built on the idea that you can have powerful AI insights while strictly adhering to data residency and privacy laws. We use federated learning—where the AI goes to the data, rather than the data being moved to a central “honeypot”—to ensure privacy is baked into the architecture.
Workplace Monitoring and Employee Rights
This is perhaps the most personal front of AI powered surveillance. Some U.S. companies now legally track keystrokes, monitor home computer usage for hybrid workers, and even use AI to analyze facial expressions during interviews to predict “behavioral competencies.” In many states, there are few legal safeguards to limit this, and disclosure isn’t always required. This creates a power imbalance that can lead to a “chilling effect” on employee morale and creativity.
Scale to 7,500 Cameras with Cloud-Based AI Powered Surveillance
The future of AI powered surveillance is moving toward the “edge” and the “cloud.” Instead of heavy, expensive servers on-site, small AI-powered “boxes” or cloud-based VMS (Video Management Systems) allow even small businesses to upgrade their existing cameras with high-end intelligence.
Cloud integration allows for massive scalability—monitoring 7,500+ cameras across multiple continents from a single dashboard. But as we expand, we must ask: how do we keep this data secure? Research into AI-powered public surveillance systems suggests that the only way forward is through transparency and civil society inclusion.
Integration with Global Data Ecosystems
We see a future where surveillance data doesn’t just live in a silo. Imagine a world where public health data, environmental sensors, and multi-omic research are linked through secure, federated platforms. This would allow for a level of “societal health monitoring” that could predict outbreaks or identify environmental toxins in real-time.
Our AI for Pharmacovigilance Ultimate Guide explores this integration. By connecting disparate datasets securely, we can achieve the benefits of mass surveillance (safety, health, efficiency) without the risks of mass data collection.
AI Powered Surveillance: 3 Questions Every Security Lead Must Answer
What are the main technical limitations of current AI surveillance?
While powerful, AI powered surveillance isn’t perfect. False positives still occur, especially in crowded environments or poor lighting. Environmental challenges like heavy rain or snow can degrade image quality, making it harder for the AI to “see” clearly. Furthermore, these systems require massive amounts of high-quality data to train the models properly, which can be a barrier for smaller organizations.
Is AI-powered surveillance legal in the workplace?
In many regions, including much of the USA, workplace surveillance is largely legal, provided it doesn’t violate specific privacy pockets (like bathrooms). However, the “how” matters. Many jurisdictions are starting to require disclosure, and new privacy bills are being introduced to limit the tracking of keystrokes or facial expressions without explicit consent.
How does AI surveillance differ from traditional CCTV?
Traditional CCTV is reactive—you watch the tape after the robbery. AI powered surveillance is proactive. It analyzes footage in real-time, recognizes threats, and alerts you while the event is happening. It replaces human observation (which fails after 20 minutes) with consistent, 24/7 machine intelligence.
Upgrade to AI Powered Surveillance: 3 Steps to Secure Monitoring
The “Big Brother Upgrade” is inevitable, but its direction is not. We have a choice. We can use AI powered surveillance to create a transparent, safe, and healthy society, or we can use it to build a digital panopticon.
At Lifebit, we choose the former. We believe the future of AI is federated. By keeping data where it lives and bringing the analysis to the data, we can harness the power of AI to protect people—whether from a physical threat in a parking lot or a biological threat in a new medication—without ever compromising their fundamental right to privacy.
Responsible implementation requires three things:
- Transparency: People must know when and how they are being monitored.
- Accountability: There must be human oversight for every AI-driven decision.
- Privacy by Design: Systems must be built to minimize data collection and maximize security.
The future of security is already here. Let’s make sure it’s a future we actually want to live in.
Ready to see how federated AI can transform your data safety?
CTA: Lifebit Federated Biomedical Data Platform

