Secure Data Fabric 101: Why Your Security Stack is Fraying

Stop Data Sprawl: How to Secure 100+ Data Silos Without Moving a Byte
A secure data fabric is a unified architecture that integrates data management, access control, and security policies across distributed environments—enabling organizations to find, classify, monitor, and protect data at scale without moving it. Here’s what you need to know:
- What it solves: Data sprawl, multicloud security gaps, compliance complexity, and siloed visibility
- How it works: Combines metadata management, automated governance, and real-time monitoring across hybrid and multicloud environments
- Key benefits: Unified visibility, zero trust enforcement, automated compliance, and reduced operational costs
- Core capabilities: Data discovery, classification, activity monitoring, encryption, and AI-driven analytics
Traditional security architectures are breaking. Over 60% of enterprise data sits unused in silos, security teams juggle over 100 disparate tools, and multicloud environments have expanded attack surfaces faster than security teams can protect them. Manual onboarding takes weeks, compliance audits drain resources, and shadow IT creates blind spots that threat actors exploit.
Secure data fabric solves this by creating a single control plane over all your data—wherever it lives. Instead of copying data into centralized warehouses or stitching together dozens of point solutions, a secure data fabric applies consistent policies, encryption, and access controls across on-premises, cloud, and edge environments. It unifies visibility, automates governance, and enables zero trust at scale.
Leading organizations are already seeing results. Modern data security fabrics protect over 500,000 business-critical databases across 200 data repositories, while AI-driven configuration has reduced onboarding time by up to 90% for teams managing multi-tenant environments. Financial services firms use secure data fabrics to detect fraud in real time, healthcare organizations maintain HIPAA compliance across federated datasets, and government agencies secure classified data across multiple security domains.
I’m Maria Chatzou Dunford, CEO and Co-founder of Lifebit, where I’ve spent over 15 years building secure data fabric architectures for biomedical research and precision medicine. At Lifebit, we enable pharmaceutical organizations and public sector institutions to run federated AI analytics across sensitive genomic and clinical datasets without moving data, proving that secure data fabric principles can open up breakthrough insights while maintaining compliance.
Secure data fabric vocab to learn:
What is a Secure Data Fabric and Why Traditional Architectures Fail?
A secure data fabric is more than just a fancy way to store files. It is a unified architecture that weaves together disparate data sources—on-premises, multicloud, and edge—into a single, cohesive layer. Unlike traditional architectures that rely on moving data into a central repository (like a data warehouse or a static data lake), a secure data fabric uses active metadata management to understand where data is, what it contains, and who should have access to it in real time.
Traditional architectures are failing because they were built for a “perimeter” world that no longer exists. When data is siloed across different departments and cloud providers, security teams lose visibility. You can’t protect what you can’t see. This “dark data”—which accounts for up to 60% of enterprise information—becomes a massive liability. A secure data fabric shines a light on these silos, integrating them without requiring expensive and risky data migration.
The Shift from Passive to Active Metadata
At the heart of this failure is the reliance on “passive metadata.” In older systems, metadata was a static catalog—a library card that told you where a book was, but didn’t tell you if someone was currently ripping out the pages. A secure data fabric utilizes active metadata. This is a continuous loop of information that tracks how data is being used, who is accessing it, and the context of that access. By applying machine learning to these metadata streams, the fabric can automatically detect when a user’s behavior deviates from the norm, such as an analyst suddenly downloading thousands of records they’ve never accessed before.
| Feature | Traditional Data Fabric | Secure Data Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Data integration and performance | Data security, privacy, and compliance |
| Access Control | Perimeter-based (Firewalls) | Zero Trust (Attribute-Based Access Control) |
| Visibility | Operational metadata | Security telemetry + Business context |
| Compliance | Manual reporting | Automated, continuous monitoring |
| Data Movement | Frequent ETL/Copying | Federated (Data stays in place) |
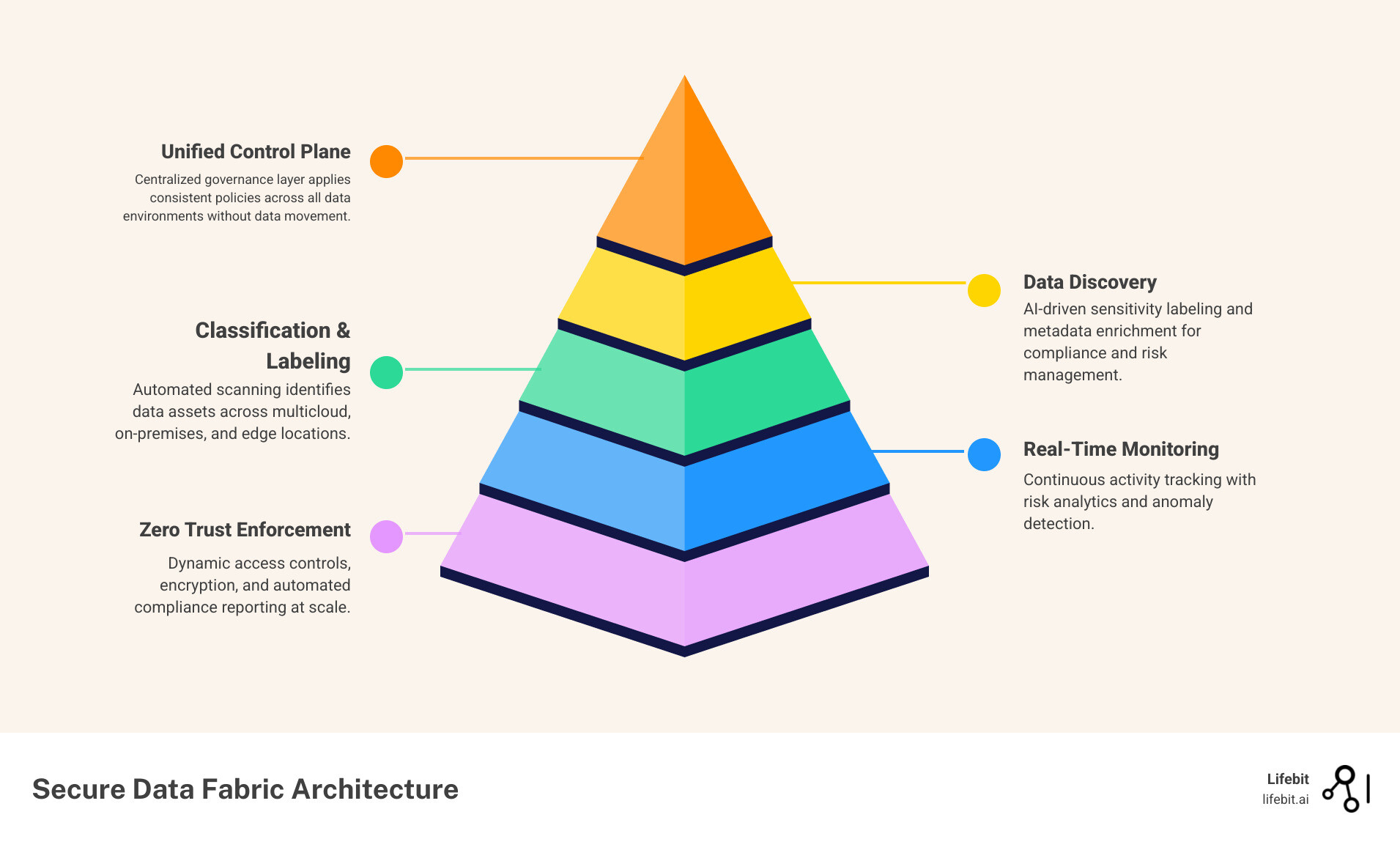
Core Components of a Secure Data Fabric Architecture
To function effectively, a secure data fabric must possess several core capabilities that transform it from a simple connector into a security powerhouse:
- Data Discovery: Automatically scanning your entire estate—including structured databases (SQL, Oracle) and unstructured files (PDFs, IoT logs)—to find sensitive information. This discovery is not a one-time event but a continuous process that identifies new data as soon as it is created.
- Classification: Labeling data based on its sensitivity (e.g., PII, PHI, or intellectual property). Modern fabrics use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand the context of data, distinguishing between a random string of numbers and a Social Security Number.
- Activity Monitoring: Tracking every request and access attempt in real time. This creates a comprehensive audit trail that is essential for forensic investigations and regulatory reporting.
- Risk Analytics: Using AI to prioritize risks. Instead of overwhelming security teams with thousands of alerts, the fabric identifies the “toxic combinations”—for example, a database that contains sensitive PII, has an open vulnerability, and is being accessed from an unusual IP address.
The Evolution of Security Data Fabric
The modern secure data fabric has evolved to bridge the gap between “security data” (logs, alerts) and “business data” (customer records, research). By enriching security telemetry with business context, teams can move away from chasing thousands of low-level alerts and focus on the threats that actually matter. This evolution relies heavily on federated data analysis. Instead of pulling all data into one spot, the fabric normalizes data at the source. It uses “entity resolution” to create a unified view of a user or an asset across multiple systems. For example, it can link a suspicious login on a cloud app to a database query on an on-premises server, providing a complete timeline for incident response.
Solving the Multicloud Security Crisis with Unified Visibility
As organizations expand into hybrid and multicloud environments, the attack surface grows exponentially. Each cloud provider—AWS, Azure, Google Cloud—has its own native security tools, creating a “fragmented” defense. This fragmentation leads to “policy drift,” where security rules are updated in one cloud but forgotten in another. A secure data fabric acts as a universal translator, providing a single dashboard to manage security across all environments, ensuring that a “High Sensitivity” label in Azure carries the same protections in AWS.
One of the biggest problems in multicloud security is deployment. Traditional “agent-based” security requires installing software on every single server—a nightmare for scalability and a frequent cause of system crashes. Modern secure data fabric solutions favor agentless deployment. By connecting directly to cloud APIs and using sidecar architectures, these fabrics provide 100% coverage across hundreds of data repositories without slowing down performance or requiring maintenance windows.
How Secure Data Fabric Enables Zero Trust at Scale
The philosophy of “never trust, always verify” is the heart of a secure data fabric. It integrates with your Microsoft Entra ID or other identity providers to ensure that every interaction is authenticated. However, the fabric goes beyond simple identity by implementing Micro-segmentation at the Data Layer.
- Least Privilege & ABAC: Using Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC), the fabric ensures users only see the specific data they need. Unlike Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), which is often too broad, ABAC looks at attributes: “Can this user (Role: Researcher) access this file (Type: Genomic Data) during business hours (Time: 9-5) from a secure VPN (Location)?”
- Conditional Access: You can set rules that block access if a user is logging in from an unknown location or an unmanaged device. The fabric can also enforce “Just-in-Time” (JIT) access, granting permissions only for the duration of a specific task.
- Multifactor Authentication (MFA): This is enforced at the fabric layer, adding a critical barrier against credential theft. Even if an attacker steals a password, the fabric’s integration with MFA and biometric verification prevents unauthorized data exfiltration.
Policy-as-Code: Automating the Defense
A key advancement in secure data fabrics is the implementation of Policy-as-Code. This allows security teams to define their data protection rules in a version-controlled language (like Rego or YAML). When a new data bucket is created in the cloud, the fabric automatically detects it and applies the relevant policies based on the code. This eliminates human error and ensures that security scales at the speed of DevOps. If a developer tries to create an unencrypted database, the fabric can automatically block the action or auto-remediate the setting in real-time.
Unified Control Across Hybrid Ecosystems
Beyond just seeing the data, a secure data fabric allows you to act on it. Through ecosystem integration, the fabric connects with your existing SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) and SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) tools. If the fabric detects a breach, it can trigger automated workflows and playbooks to isolate the affected data source instantly. This reduces the “mean time to respond” (MTTR) from days to seconds, preventing a localized incident from becoming a catastrophic data breach.
Automating Compliance: GDPR, HIPAA, and Global Standards
Compliance is no longer a once-a-year event; it’s a 24/7 requirement. For industries like healthcare and finance, the manual burden of proving compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, or the newer CCPA/CPRA can be staggering. A secure data fabric automates this by providing data lineage and information protection labels that follow the data wherever it goes.
With automated auditing, you can generate reports in minutes rather than weeks. The fabric tracks the entire lifecycle of a data point: where it originated, who modified it, and who accessed it. This provides a “non-repudiable” record that satisfies even the strictest regulators. In the event of an audit, instead of scrambling to collect logs from twenty different systems, the compliance officer simply exports a unified report from the fabric.
Achieving Data Sovereignty and Residency
For global organizations, data residency—the requirement that data stays within a specific country’s borders—is a major legal hurdle, especially following rulings like Schrems II in the EU. A secure data fabric supports Multi-Geo capacities, allowing you to store and process data in specific regions while maintaining centralized management.
This is particularly vital for secure data environments (SDEs). By using customer-managed keys (CMK), organizations can ensure that even their cloud provider cannot access the raw data. This “Double Key Encryption” ensures that the organization remains the sole custodian of the data, maintaining total sovereignty over their most sensitive assets even when using third-party infrastructure.
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs) within the Fabric
Modern secure data fabrics are increasingly integrating Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs) to allow for data utility without compromising privacy. These include:
- Differential Privacy: Adding mathematical “noise” to a dataset so that individual identities cannot be reverse-engineered, while the overall statistical trends remain accurate.
- Homomorphic Encryption: Allowing computations to be performed on encrypted data without ever decrypting it. This is the “holy grail” of data security, enabling a third party to analyze data without ever seeing the underlying sensitive information.
- Dynamic Data Masking: Redacting sensitive fields (like credit card numbers) in real-time based on the user’s permissions. A customer service rep might see only the last four digits, while a billing manager sees the full number.
Encryption at Rest and in Transit
A robust secure data fabric ensures that data is never exposed, regardless of its state.
- Encryption at Rest: Data is automatically encrypted using AES-256 or similar standards. The fabric manages the rotation of these keys to prevent long-term exposure.
- Encryption in Transit: All communication between the user and the fabric, or between different nodes of the fabric, is protected by TLS 1.2 or 1.3. This prevents “man-in-the-middle” attacks where hackers intercept data as it moves across the network.
- Key Management: Integration with services like Azure Key Vault or HashiCorp Vault allows organizations to manage their own encryption keys, providing an extra layer of “lockbox” security that separates the data from the keys.
Real-World Impact: From Healthcare to Financial Services
The theoretical benefits of a secure data fabric are impressive, but the real-world applications are where the technology truly shines. By removing the need to move data, organizations can collaborate in ways that were previously impossible due to security risks.
Healthcare: Breakthroughs via Federated AI
In healthcare, researchers use Trusted Research Environments (TREs) built on data fabric principles to analyze patient genomic data without ever moving it out of the hospital’s secure servers. This is critical because genomic data is uniquely identifiable and highly sensitive.
Using Federated Learning, a secure data fabric allows an AI model to travel to the data, learn from it locally, and then return to a central hub with only the “insights” (the model weights), never the actual patient records. This allows for massive, multi-site studies across different countries while strictly adhering to local patient privacy laws. For example, a pharmaceutical company can train a cancer-detection model on datasets from ten different hospitals across Europe without any data ever leaving the hospital firewalls.
Financial Services: Real-Time Fraud Prevention
In financial services, banks use the fabric to unify data from thousands of branches, mobile apps, and third-party payment processors. This enables real-time fraud detection at a scale that traditional systems can’t match. By analyzing patterns across the entire fabric, a bank can identify a coordinated “credential stuffing” attack as it happens. For instance, a top retailer prevented 10,000 attacks in just the first four hours of a Black Friday weekend using these high-scale monitoring capabilities. The fabric allowed them to see the connection between seemingly unrelated login attempts across different regions, identifying the botnet’s signature.
Government and Space: Managing Classified Data
Even in government and defense, the technology is critical. Agencies use secure fabrics for Space Traffic Management, sharing sensor data across different classification levels (unclassified to top secret) without risking data leakage. The fabric ensures that a user with “Secret” clearance can see the trajectory of a satellite, but only a user with “Top Secret” clearance can see the specific sensor data that generated that trajectory. This granular control allows for international cooperation in space while protecting national security interests.
AI and Machine Learning in Modern Secure Data Fabric
AI is the “secret sauce” that makes modern fabrics scalable. AI-driven configuration can reduce the time it takes to onboard a new data source by up to 90%. Instead of a human engineer manually mapping fields and setting permissions, the AI analyzes the data structure, identifies sensitive fields, and suggests the best security policies automatically.
Machine learning also powers anomaly detection. By learning the “normal” behavior of every user and application, the fabric can spot a “low and slow” data exfiltration attempt—where an attacker steals small amounts of data over a long period—that would bypass traditional threshold-based alerts.
Scaling Security Operations for Large Enterprises
For an enterprise with petabytes of data, “manual” security is an impossibility. A secure data fabric uses modular pipelines to route data efficiently. It supports multi-tenant isolation, ensuring that different departments, subsidiaries, or customers within the same organization can’t peek at each other’s data. This operational discipline turns security from a bottleneck into a competitive advantage, allowing businesses to launch new data-driven products faster and with more confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions about Secure Data Fabric
How does a secure data fabric reduce operational costs?
By consolidating dozens of point solutions into a single data governance platform, organizations reduce licensing fees and the “talent tax” of training staff on 100 different tools. Automation of manual tasks—like auditing and classification—frees up high-value security engineers to focus on threat hunting rather than paperwork.
Can a secure data fabric handle unstructured data?
Yes. Leading fabrics can support over 1,500 file formats and data types. This includes everything from standard SQL databases to “dark data” like PDFs, images, and sensor logs. By extracting metadata from these files, the fabric makes them searchable and governable for the first time.
What is the difference between a data lake and a secure data fabric?
A data lake is a storage destination—a place where you dump data. A secure data fabric is an active access layer. While a data lake is often static and requires data to be moved into it, a fabric connects to data where it lives. A fabric also includes built-in governance, whereas data lakes often require additional tools to manage permissions and security.
Conclusion: Future-Proofing Your Data Estate
The “old way” of securing data—building higher walls around your data center—is over. In a world of multicloud sprawl and AI-driven threats, you need a security strategy that is as fluid and distributed as your data itself.
At Lifebit, we believe that the future of research and innovation depends on federated data governance. Our platform, including the Trusted Data Lakehouse, is built on the core principles of the secure data fabric. We enable global biopharma and public health agencies to access multi-omic data in real time, ensuring that security and compliance are never sacrificed for the sake of speed.
By adopting a secure data fabric, you aren’t just fixing a “fraying” security stack—you’re building a foundation for the next decade of secure, data-driven growth.

