The Best Biotech Companies in London for Data Analytics

Why London Leads in Data-Driven Biotech Innovation
What are the top biotech companies in London that focus on data analytics? London is home to several pioneering biotech companies leveraging AI, machine learning, and computational biology to transform drug findy. Here are the leading players:
- BenevolentAI – Uses AI and machine learning across every step of drug findy, combining computational power with scientific expertise to decipher disease biology
- Isomorphic Labs – Applies DeepMind’s AlphaFold3 technology to reimagine digital drug findy using artificial intelligence
- Relation Therapeutics – Integrates single-cell analysis, genomics, and machine learning in a ‘Lab-in-the-Loop’ approach to map human biology
- LabGenius – Employs a machine learning-driven evolution engine combined with robotics to engineer next-generation protein therapeutics
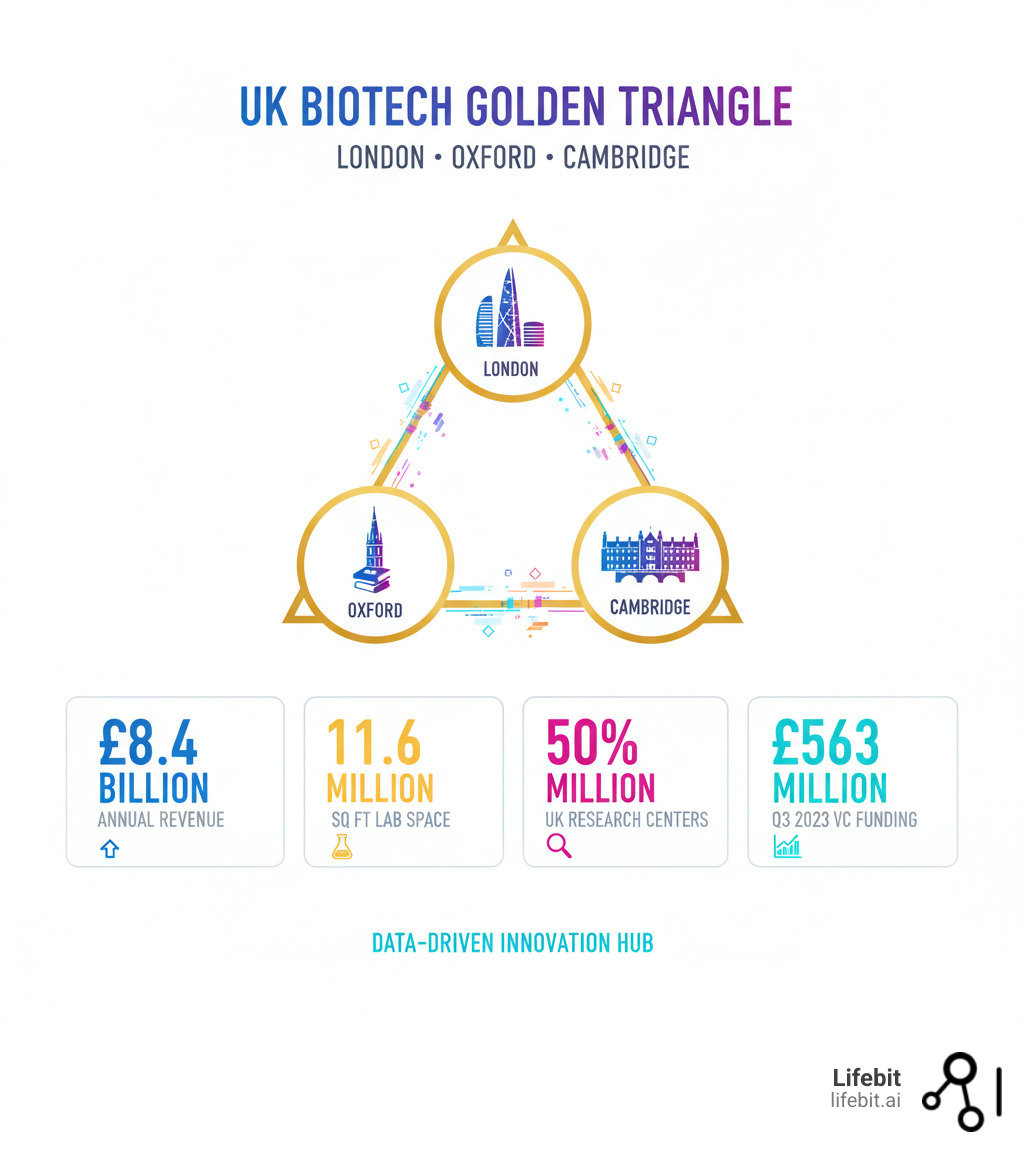
These companies represent London’s position as a global hub for data-driven biotech innovation, sitting at the heart of the UK’s ‘golden triangle’ alongside Oxford and Cambridge.
The UK remains the leader of European biotech efforts, securing £563 million in venture capital and public financing in Q3 2023 alone—a 49% increase from the previous quarter. London plays a central role in this ecosystem, hosting approximately half of all UK-based research centers within the golden triangle, which spans 11.6 million square feet of laboratory space and generates about £8.4 billion per annum.
What sets London apart is the rapid integration of AI and data analytics into traditional biotechnology. Companies are no longer just running lab experiments—they’re building computational platforms that analyze massive datasets, predict protein structures, and identify drug targets with unprecedented speed and accuracy. This shift is attracting global investment and partnerships with pharmaceutical giants.
As Maria Chatzou Dunford, CEO and Co-founder of Lifebit with over 15 years of expertise in computational biology and AI, I’ve witnessed how London’s top data-focused biotech companies are reshaping global healthcare through federated data analysis and secure, compliant research environments. The companies featured in this article represent the cutting edge of this change.
What are the top biotech companies in London that focus on data analytics?
The world of drug findy is changing—fast. Gone are the days when researchers spent decades in the lab, testing compounds one by one, hoping to stumble upon a breakthrough. Today’s biotech leaders are combining the power of AI, machine learning, and computational biology with traditional lab work to decode disease in ways we never thought possible.
This shift from wet-lab-only approaches to big data analysis isn’t just about working faster. It’s about fundamentally reimagining how we understand human biology and design treatments. The companies leading this revolution? Many of them call London home.
BenevolentAI: Decoding Disease Biology with AI
When BenevolentAI launched in 2013, they had a bold vision: use artificial intelligence to decipher the complex puzzle of human disease. More than a decade later, they’ve built one of the most comprehensive computational R&D platforms in the industry.
Their approach touches every step of the drug findy process. By analyzing vast datasets—scientific literature, clinical trial results, biomedical information—their machine learning algorithms identify promising drug targets and potential therapeutic compounds that human researchers might miss. It’s like having a tireless research assistant who’s read every medical paper ever published and can spot patterns across millions of data points.
The market has taken notice. In 2022, BenevolentAI completed the largest ever European SPAC merger, a deal that underscored investor confidence in their AI-driven approach. They’re not just building tools for others either—their in-house drug pipeline demonstrates their commitment to turning computational insights into real medicines that help real patients.
Isomorphic Labs: Applying DeepMind’s AI to Reimagine Drug Findy
If you’ve heard of AlphaFold—the AI that can predict protein structures with stunning accuracy—then you already know part of Isomorphic Labs’ story. Established in 2021 and spun out of Google DeepMind, this London biotech is applying some of the world’s most advanced AI to completely reimagine how we find drugs.
The connection to AlphaFold3 is particularly exciting. Understanding how proteins fold and interact is fundamental to drug design. For decades, determining protein structures required expensive equipment and months of painstaking work. Now, AI can predict these structures in hours.
Isomorphic Labs’ AI-first approach has attracted serious attention from pharmaceutical giants. In early 2024, they announced strategic collaborations with Eli Lilly and Novartis—partnerships potentially worth nearly $3 billion.
Relation Therapeutics: Mapping Human Biology with Machine Learning

Human biology is messy and interconnected in ways we’re only beginning to understand. Relation Therapeutics is tackling this complexity head-on with their innovative “Lab-in-the-Loop” approach that seamlessly blends laboratory work with advanced computational analysis.
Their platform combines single-cell analysis, genomics, and proteomics with sophisticated graph machine learning algorithms. By analyzing patient tissue at the cellular level and integrating multiple types of biological data (multi-omics), they can map the intricate networks of genes, proteins, and cells that drive disease. This helps them identify novel drug targets that traditional methods might overlook.
The company is currently focused on osteoporosis, but their approach has broader implications for understanding complex diseases. Their partnership-driven model includes collaborations with tech giants like NVIDIA, bringing cutting-edge computing power to biological questions. In April 2024, they secured $35 million in seed funding—a strong vote of confidence for their data-driven approach to finding new medicines.
LabGenius: Engineering Next-Gen Proteins with a ML-Driven Engine
LabGenius has built something special: a platform called EVA that brings together machine learning, synthetic biology, and robotics into one seamless drug findy engine. Think of it as an automated laboratory that can design, test, and refine protein therapeutics at unprecedented speed.
The EVA platform enables automated drug engineering, allowing LabGenius to rapidly iterate through thousands of protein variants. Instead of manually designing and testing each candidate—a process that could take years—they use machine learning to predict which designs are most promising, then let robots handle the actual testing.
This integration of data analytics and automation is particularly powerful for antibody findy and developing next-generation protein therapeutics. By combining computational design with high-throughput robotic experimentation, LabGenius can compress timelines and explore a much larger design space than would be possible with traditional methods.
These four companies represent the cutting edge of what London’s top data-focused biotech companies are achieving. They’re not just using data to work faster—they’re using it to ask entirely new questions and find answers that weren’t previously possible.
How Data Analytics is Revolutionizing London’s Biotech Ecosystem
Something remarkable is happening in London’s biotech labs. Data analytics isn’t just supporting traditional research anymore—it’s fundamentally reshaping how we find and develop new medicines. The companies we’ve explored are proving that computational power, when combined with biological insight, can tackle problems that seemed unsolvable just a few years ago.
The impact is tangible and measurable. Drug findy timelines that once stretched across 10-15 years are being compressed. Research and development costs, traditionally measured in billions, are dropping significantly. Clinical trial success rates, historically around 10%, are improving as better data helps identify the right patients and the right targets from the start. And perhaps most exciting, precision medicine—treatments custom to individual genetic profiles—is moving from theory to reality. This acceleration is not merely about speed; it’s about increasing the probability of success at each stage of the R&D pipeline, a concept known as ‘de-risking’ drug development. By using data to make more informed decisions earlier, companies can avoid costly late-stage failures.
What are the key data analytics approaches used by these London biotech companies?
When you look at London’s top data-focused biotech companies, you’ll notice they’re all using similar foundational technologies, but in remarkably different ways to build a competitive edge.
AI and machine learning algorithms form the backbone of modern biotech research. These systems excel at spotting patterns in biological data that human researchers might miss. They can predict how a drug molecule will interact with a protein target, identify subtle biomarkers that signal disease progression, and even forecast which patients will respond best to specific treatments. A significant recent development is the application of generative AI. Going beyond pattern recognition, generative models can design entirely novel entities, such as new protein sequences with specific functions or small molecules with desired therapeutic properties. This allows companies to explore a vast, uncharted chemical space, creating potential drug candidates that would never be conceived through traditional chemistry. At Lifebit, we’ve seen how AI-powered diagnostics and AI healthcare UK solutions are bringing precision medicine closer to clinical reality every day.
Computational biology takes this further by building detailed models of biological systems. Think of it as creating a digital twin of a protein, a cell, or even an entire biological pathway. Technologies like AlphaFold3 can now predict protein structures with stunning accuracy, allowing researchers to design drugs that fit their targets like a key in a lock—all before stepping into a physical lab. This ‘in silico’ experimentation is expanding beyond single proteins. Researchers are now building complex models of cellular signaling pathways to simulate how a disease progresses and how a potential drug might intervene. These simulations can predict off-target effects and potential toxicity, providing crucial insights long before a compound is tested in living organisms.
The challenge, of course, is that biological data comes in countless forms. Genomic sequences, protein measurements, clinical records, medical images, real-world patient data—the list goes on. Big data platforms solve this by integrating these diverse data types into unified systems where they can be analyzed together. This is more than just storage; it involves creating a ‘data fabric’ that harmonizes disparate formats and standards. For example, a platform might need to link a patient’s genomic data from a sequencing lab, their electronic health record from a hospital, and their wearable device data. It’s this holistic, longitudinal view of a patient that often reveals the most valuable insights into disease mechanisms and treatment responses.
Multi-omics analysis has become particularly powerful. Rather than looking at just genetics (genomics) or just proteins (proteomics), researchers now analyze multiple biological layers simultaneously. This provides a complete picture of what’s happening in diseased tissue, revealing connections that single-layer analysis would miss entirely. For instance, in oncology, a multi-omics approach might combine genomics to identify cancer-driving mutations, transcriptomics to see how those mutations affect gene expression, proteomics to observe the resulting changes in protein activity, and metabolomics to understand the downstream impact on cellular metabolism. By layering these datasets, researchers can build a highly detailed map of a tumor’s unique biology, paving the way for truly personalized therapies.
Even scientific literature itself has become a data source. Natural language processing (NLP) algorithms can read through millions of research papers, patents, and clinical trial reports, extracting insights and identifying connections that would take human researchers years to uncover. This helps scientists quickly synthesize vast amounts of information and spot emerging patterns across disciplines. Advanced NLP models can now go beyond simple keyword extraction to understand context, identify relationships between genes, diseases, and compounds, and even generate hypotheses for further investigation. This turns the entire body of published scientific knowledge into a queryable database, accelerating the earliest stages of discovery.
What are the primary therapeutic focuses for these data-driven biotechs?
The beauty of data-driven approaches is that they’re especially valuable where diseases are most complex. That’s why London’s biotech companies are concentrating their efforts on some of medicine’s toughest challenges.
Oncology remains a primary focus. Cancer’s genetic complexity makes it an ideal target for AI and computational biology. These tools help identify new therapeutic targets, design personalized immunotherapies (like CAR-T cells), predict which patients will respond to chemotherapy, and understand the mechanisms of acquired resistance. For example, AI can analyze tumor biopsy images to identify patterns invisible to the human eye that correlate with patient outcomes, a field known as computational pathology.
Neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s have frustrated researchers for decades. The brain’s complexity and the difficulty of obtaining tissue samples demand computational approaches to solve disease mechanisms. By analyzing genetic data from large patient cohorts alongside brain imaging and cognitive data, AI models can identify early risk factors and disease subtypes. Companies like Isomorphic Labs and Relation Therapeutics are using data analytics to map these intricate neural and molecular pathways and identify therapeutic opportunities that traditional methods might never find.
For rare genetic diseases, where patient populations are small and traditional clinical trials are challenging, genomic data analysis becomes essential. Data-driven approaches enable accurate diagnosis, often ending a long ‘diagnostic odyssey’ for patients. They also reveal disease mechanisms and help develop gene therapies or precision treatments custom to specific genetic mutations. By aggregating data from patients globally (often using federated approaches to protect privacy), researchers can achieve the statistical power needed to understand these conditions and test new therapies.
Inflammatory and autoimmune conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and psoriasis, also benefit enormously from data analytics. These diseases result from complex dysregulation of the immune system. Understanding the intricate interactions between different immune cells, signaling molecules (cytokines), and genetic predispositions requires computational modeling. This knowledge enables the development of highly targeted therapies, like monoclonal antibodies, that can control inflammation precisely, without the broad side effects of traditional immunosuppressive drugs. Multi-omics analysis of patient samples can also help stratify patients into groups that are more likely to respond to a particular biologic drug.
By focusing data analytics on these complex, difficult-to-treat diseases, London’s biotech companies are pushing medicine into territories that seemed unreachable just a few years ago. They’re not just making incremental improvements—they’re reimagining what’s possible in healthcare.
Frequently Asked Questions about London’s Data-Centric Biotech Scene
Why is London a major hub for biotech and data analytics?
London didn’t become a powerhouse for biotech and data analytics by chance. It’s the result of several factors coming together in just the right way.
First, there’s the academic excellence. London is home to world-renowned universities like University College London (UCL), King’s College London, and Imperial College London. These aren’t just prestigious names—they’re actively producing groundbreaking research and training the next generation of scientists who understand both biology and data science. Add in institutions like The Francis Crick Institute, one of the world’s leading biomedical research centers, and you have an environment where scientific innovation thrives.
The city also offers unparalleled access to capital. As a global financial center, London connects biotech startups with venture capital firms, public financing, and private equity investors who understand the long-term potential of data-driven drug findy. This matters enormously in biotech, where bringing a new therapy to market can take years and significant investment.
Then there’s the government support. The UK government has made life sciences a strategic priority, backing the sector with funding initiatives and policies that encourage innovation in AI and data analytics. The UK ranks third globally for AI ‘vibrancy’ according to Stanford research, reflecting a supportive environment for companies working at the intersection of biology and technology.
London’s status as a global city means it attracts talent from around the world. You’ll find computational biologists from one country working alongside chemists, data scientists, and clinicians from others. This diversity of expertise and perspective is exactly what’s needed to solve complex biological problems using advanced analytics.
Finally, there are the innovation districts like the Knowledge Quarter around King’s Cross. These areas bring together laboratory space, incubators, and collaborative environments where ideas can cross-pollinate. The London BioScience Innovation Centre (LBIC), London’s first bio incubator located in the Knowledge Quarter, exemplifies how these districts turn scientific findy into commercial success.
What is the ‘golden triangle’ in UK life sciences?
If you’re exploring London’s top data-focused biotech companies, you’ll quickly encounter references to the ‘golden triangle.’ This isn’t marketing speak—it’s a genuinely world-leading life sciences cluster formed by London, Oxford, and Cambridge.
What makes this triangle so powerful is how it combines academic excellence, research centers, and commercial biotech in close geographical proximity. You have some of the world’s top universities conducting fundamental research, specialized institutes pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, and a high concentration of biotech companies turning those findies into treatments.
The numbers tell the story. This ecosystem generates £8.4 billion per annum and spans 11.6 million square feet of laboratory space. London sits at the heart of this network, home to about half of all UK-based research centers within the golden triangle.
What’s particularly valuable about this arrangement is the flow of knowledge and talent between the three cities. A researcher might train at Cambridge, work on a project at a London institute, and then collaborate with an Oxford spinout. This interconnectedness accelerates innovation in ways that wouldn’t be possible if these hubs were isolated.
The golden triangle has become a magnet for investment, attracting both domestic and international capital looking to back the next breakthrough in data-driven drug findy. For companies working in this space, being part of this ecosystem provides access to resources, expertise, and partnerships that would be difficult to replicate elsewhere.
What challenges do these companies face in leveraging data analytics?
Despite all the advantages London offers, companies working at the intersection of biotech and data analytics face real challenges. Understanding these obstacles helps explain why solutions like secure federated platforms have become so important.
Data access remains one of the biggest problems. Biomedical data sits scattered across hospitals, research institutions, universities, and private companies, often locked in separate systems that don’t communicate with each other. A company trying to build a comprehensive dataset for training AI models might need to negotiate with dozens of organizations, each with different policies and technical infrastructures. Getting secure and ethical access to these diverse datasets, and then integrating them into something usable, is far more complex than it sounds.
Even when you can access data, there’s the problem of quality and standardization. One hospital might record patient information differently than another. Lab results might use different units or reference ranges. Genetic data might be processed using different pipelines. These inconsistencies can compromise analytical insights or require extensive data cleaning and harmonization before any meaningful analysis can begin.
Then there are the regulatory challenges. Patient data is rightly protected by strict privacy regulations like GDPR. Companies need to ensure they’re handling sensitive information in ways that protect patient privacy while still enabling the advanced analytics that can lead to breakthrough treatments. This requires sophisticated technical solutions, robust legal frameworks, and constant vigilance to maintain compliance as regulations evolve.
Perhaps most challenging is the talent gap. Finding professionals who deeply understand both life sciences and advanced data science is difficult. You need people who can speak the language of biology and medicine while also being proficient in AI/ML, computational statistics, and software engineering. Building interdisciplinary teams with this rare combination of skills takes time and resources, and competition for these individuals is fierce.
These challenges aren’t impossible, but they do require thoughtful solutions. At Lifebit, we’ve built our federated AI platform specifically to address many of these obstacles—enabling secure access to distributed data, providing built-in harmonization capabilities, ensuring regulatory compliance, and making advanced analytics accessible to researchers regardless of their technical background.
Conclusion: The Future of Biotech is Secure, Federated, and AI-Powered

London’s biotech sector stands at the forefront of a remarkable change. What are the top biotech companies in London that focus on data analytics? The answer reveals a landscape where AI and computational power are fundamentally reshaping how we find medicines and understand disease. From BenevolentAI’s comprehensive computational platform to Isomorphic Labs’ groundbreaking protein structure predictions, from Relation Therapeutics’ graph machine learning to LabGenius’ automated protein engineering—these pioneers are proving that the future of healthcare lies in the intelligent application of data.
These companies aren’t just incremental improvements on old methods. They represent a complete reimagining of drug findy, one where vast datasets, sophisticated algorithms, and biological expertise converge to tackle diseases that have long resisted traditional approaches. Their success stories underscore London’s vital position within the UK’s golden triangle and its growing reputation as a global innovation powerhouse.
Yet for all this progress, the real breakthroughs still lie ahead. The most pressing challenge isn’t developing better algorithms or more powerful AI—it’s enabling secure collaboration across the massive, distributed datasets that hold the answers to our most complex health questions. Data sits locked in silos across hospitals, research institutions, and private companies. Regulatory requirements, while essential for protecting patient privacy, create additional barriers to the kind of large-scale analysis that could accelerate findies.
This is where the concept of federated analysis becomes transformative. Instead of moving sensitive data to centralized locations—with all the security risks and compliance headaches that entails—federated approaches bring the analysis to the data. Researchers can derive insights from global datasets while each institution maintains full control over its information.
At Lifebit, we’ve built our platform around this vision. Our next-generation federated AI platform enables secure, real-time access to global biomedical and multi-omic data without compromising privacy or regulatory compliance. With built-in capabilities for data harmonization, advanced AI/ML analytics, and federated governance, we power the kind of large-scale, compliant research that biopharma companies, government agencies, and public health organizations need to make genuine breakthroughs.
Our platform components—including our Trusted Research Environment (TRE), Trusted Data Lakehouse (TDL), and R.E.A.L. (Real-time Evidence & Analytics Layer)—work together to deliver real-time insights, AI-driven safety surveillance, and secure collaboration across hybrid data ecosystems. This means the innovative work being done by London’s top biotech companies can scale globally, accessing the diverse datasets needed to develop treatments that work for everyone, not just specific populations.
The future of biotech is being written right now in London’s labs and offices. It’s a future where AI and human expertise work hand in hand, where data flows securely across borders and institutions, and where the next generation of life-changing medicines emerges faster than ever before. Discover how a federated platform can accelerate your research and join us in building that future.

