Clinical Research Analytics: Decoding the Future of Medicine

Every Day Lost in Clinical Trials Costs Lives—Here’s How Data Analytics Fixes It
Clinical research data analytics is the process of analyzing data from clinical trials to generate evidence that speeds new therapies to patients, improves trial design, and ensures patient safety. It involves collecting data from sources like EHRs and genomics, cleaning and integrating it, applying statistical and AI-powered analysis, and translating findings into action.
Why does this matter? The success rate for new drugs is a dismal 6.1%, and Phase III trial timelines have ballooned by 47% over the last 20 years. Every delay costs lives. Modern data analytics—powered by AI and federated technology—is our best tool to reverse this trend, cutting timelines and delivering safer therapies faster.
I’m Maria Chatzou Dunford, CEO and Co-founder of Lifebit. With over 15 years in computational biology and AI, I’ve seen how real-time, secure data analysis can open up breakthroughs. In this guide, you’ll learn how modern analytics solves the biggest challenges in clinical research and how you can leverage these tools to make a real impact.

Why Outdated Clinical Research Analytics Are Draining Budgets and Delaying Cures
The traditional approach to clinical trial data is failing us—and it’s costing lives.
The numbers are sobering: the success rate for new molecular entities (NMEs) is just 6.1%. For every 100 potential drugs, fewer than seven reach patients. Worse, Phase III trial timelines have increased by 47% over the last 20 years. Every day a trial is delayed, patients with cancer, rare diseases, and chronic conditions run out of time.
Clinical research data analytics is the bridge between mountains of trial data and the medical breakthroughs patients desperately need. Our deeper explorations of Clinical Research Data Analytics and Clinical Trial Data show exactly how this change happens.
The Real Goal: Turn Raw Data Into Breakthroughs That Save Lives
Think of analytics as turning raw, messy data into insights that save lives. The process involves:
- Data Collection: Gathering information from patient surveys, lab tests, EHRs, and genomic sequencing.
- Data Cleaning: The critical work of correcting errors, standardizing formats, and removing duplicates. Without this, analysis is useless.
- Analysis & Interpretation: Using statistics and clinical expertise to identify trends and correlations that would otherwise stay hidden.
The ultimate goal is to support decisions with evidence, helping providers refine treatments and regulators approve safe, effective therapies faster.
Why Old-School Methods Fail: The Hidden Risks
Traditional data management is riddled with problems that undermine medical progress:
- Data Silos: Information is trapped in isolated systems, making a complete picture impossible. Imagine a patient’s genomic data is in a research lab’s database, their clinical trial data is with a CRO, and their longitudinal health record is in a hospital’s EHR. Without a unified view, it’s impossible to correlate a specific gene with a drug response observed in the trial. It’s like trying to solve a puzzle with half the pieces locked in different rooms.
- Poor Interoperability: Different data formats and software systems don’t communicate. Clinical data may be in CDISC format, while hospital data uses HL7 or FHIR, and genomic data has its own standards. The lack of a common data model turns integration into a nightmarish, error-prone manual mapping effort that consumes vast resources and time.
- Slow, Manual Analysis: Time-consuming manual processes delay critical insights for weeks or months. Data is often exported to spreadsheets or local SAS environments where statisticians write custom, one-off scripts. Any change in the data or a new question requires re-running the entire process manually, introducing significant delays and a high risk of human error.
- Regulatory Bottlenecks: Necessary rules like GDPR and HIPAA are designed to protect patients, but without modern, compliant systems, they can become roadblocks. An organization’s fear of non-compliance often leads to overly restrictive data sharing policies, preventing even legitimate, anonymized data analysis that could unlock critical insights.
- Hidden Biases: Data from sources like electronic health records can contain subtle biases. Beyond “informed presence bias,” where sicker patients have more data, there’s also selection bias. RWD often over-represents populations with better access to healthcare, potentially missing data from less-privileged or rural groups. As researchers highlighted in Three risks to avoid in the rush for big data in health care, this can lead to misleading results and therapies that aren’t effective for everyone.
Overcoming these risks requires a complete overhaul of our approach to clinical research data analytics—one that breaks down silos and enables real-time, secure analysis.
How Modern Analytics Slashes Trial Timelines and Costs—And Delivers Safer, Faster Results
The good news? We’re not stuck with outdated methods. Modern clinical research data analytics offers a powerful antidote to the challenges plaguing clinical trials, dramatically reducing timelines and costs.
This change touches every stage of a trial, from protocol design and patient recruitment to safety monitoring and regulatory submission. By leveraging Real-World Data and making informed decisions, we can drive breakthroughs in Precision Medicine. Companies using advanced analytics are cutting enrollment times in half and detecting safety signals months earlier.
Cut Time to Market: Faster Enrollment, Smarter Decisions
Time is the most precious currency in clinical research. Modern analytics helps us reclaim it.
- Enrollment Optimization: Instead of casting a wide net, analytics helps predict which patients are most suitable for a trial. By analyzing EHR and claims data, platforms can build a detailed profile of the ideal participant based on complex inclusion/exclusion criteria. This allows sponsors to identify geographic hotspots with high patient concentrations and even pre-screen potential participants, drastically reducing the screen failure rate, which can be as high as 80% in some complex trials.
- Smarter Site Activation: Analytics can optimize the timing and sequence of site activation. By analyzing historical performance data, sponsors can prioritize high-enrolling sites and avoid those that consistently underperform, ensuring strategic deployment that makes every site count from day one.
- Predictive Success Modeling: Imagine knowing the likelihood of a trial’s success before it begins. Machine learning models trained on thousands of historical trials (both successful and failed) can improve drug efficacy prediction by 20%. By analyzing factors like drug mechanism, biomarker prevalence, and endpoint selection, these models allow teams to focus resources on the most promising therapies and avoid costly dead ends.
Protect Patients: Real-Time Safety and Oversight
Patient safety is non-negotiable. Modern analytics provides unprecedented capabilities for proactive risk management.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Analytics platforms provide continuous oversight, allowing teams to spot potential safety or data quality issues as they arise, not weeks later during a site visit.
- AI-Powered Anomaly Detection: AI systems automatically flag unusual trends in patient data—such as a spike in a specific lab value at one site—that might indicate a safety concern. This acts as a vigilant guardian over the trial, allowing medical monitors to visualize trends across aggregated data and identify unexpected patterns that human reviewers might miss.
- Adverse Event Prediction: By analyzing vast datasets, machine learning models can help predict which patients are at higher risk for adverse events, enabling proactive interventions and more personalized safety monitoring plans.
- Risk-Based Quality Management (RBQM): Instead of the costly and inefficient practice of 100% Source Data Verification (SDV), RBQM uses analytics to focus on the most critical risks. By tracking Key Risk Indicators (KRIs), the system automatically identifies sites that are outliers in terms of data entry errors, protocol deviations, or adverse event reporting. This targeted approach uncovers performance issues and can lead to 75% time savings in running studies, providing insights in hours instead of weeks. These advancements are part of broader Clinical Trial Technology Trends reshaping research.
Open up Real-World Data for Deeper, Cheaper Insights
Real-world data (RWD) captures what happens when patients take medications in their daily lives. Analytics helps us harness this data for faster, cheaper insights.
- External Control Arms: RWD can be used to create synthetic or external control arms (ECAs), reducing the need for placebo groups. This is especially valuable in oncology and rare disease studies where recruiting a placebo arm may be unethical or impractical. Regulatory bodies like the FDA are increasingly accepting evidence from well-designed ECAs, provided the methodology is transparent and the RWD population is comparable to the trial population.
- Trial Feasibility: Before investing millions, RWD helps answer critical questions: Are there enough patients who meet the protocol criteria? Where are they located? Analyzing RWD prevents costly design mistakes and ensures the trial is viable from the start.
- Long-Term Follow-Up: RWD allows for continuous, long-term monitoring of a therapy’s safety and effectiveness over years, far beyond the typical duration of a clinical trial. This is crucial for catching rare side effects or identifying long-term benefits that trials might miss.
As the Duke-Margolis White Paper on regulatory use of real-world evidence highlights, there’s a growing pathway for RWD to play a central role in drug development and approval. Modern clinical research data analytics is fundamentally changing how we bring new therapies to market: faster, safer, and smarter.
The AI Edge: Double Your Speed, Halve Your Risk in Clinical Research
If you’re running clinical trials without AI, you’re working twice as hard for half the results.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are no longer just buzzwords. They are the difference between a trial that takes years and one that delivers answers in months. Between spotting a safety signal before it becomes a crisis and catching it too late.

From machine learning algorithms that predict patient response to generative AI that automates tedious paperwork, these technologies are revolutionizing clinical research data analytics. This is about predictive analytics that frees your team to focus on science, not spreadsheets. Explore how AI in Clinical Trials is reshaping research, and see how AI for Drug Findy is revolutionizing pharmaceutical development.
How AI and Machine Learning Are Changing the Game
In the real world of clinical trials, AI delivers practical, budget-saving results.
- Predicting Patient Outcomes: AI models analyze diverse patient data—histories, genomics, real-world evidence, and even medical images—to predict who will respond to treatment and who is at risk for adverse events. For example, in an oncology trial, an AI model could analyze a patient’s tumor histology images alongside their genomic profile to predict their likelihood of responding to a new immunotherapy, enabling powerful patient stratification.
- Finding New Biomarkers: AI excels at spotting subtle patterns in complex, high-dimensional datasets. Unsupervised machine learning can cluster patients based on multi-omic data (genomics, proteomics, metabolomics) to identify novel subgroups who share molecular characteristics. These characteristics can then be investigated as potential predictive biomarkers for patient selection, accelerating the path to personalized medicine. Our work in AI for Genomics shows how powerful this is.
- Automating Data Review: Natural Language Processing (NLP) and generative AI can automate the time-consuming tasks of data review and reconciliation. These tools can scan unstructured data like clinical notes or adverse event narratives, extract key information, and check for consistency against structured data in the electronic Case Report Form (eCRF), identifying discrepancies in a fraction of the time.
- Optimizing Protocol Design: Before a trial even begins, AI can simulate thousands of potential outcomes based on different protocol designs. By varying inclusion/exclusion criteria, endpoints, or trial duration, sponsors can identify the optimal design that maximizes the probability of success while minimizing patient burden and cost.
As experts at Bio-IT World note in “Dam Data: Health Systems, Machines, And Learning,” machine learning lets practitioners tap into the collective experience of millions of patient records. However, AI isn’t magic; it requires clinical expertise and solid study design to turn its power into breakthroughs.
AI vs. Traditional Analytics: The Numbers That Matter
Let’s look at what AI delivers compared to traditional methods:
| Feature | Traditional Analytics | AI-Powered Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Weeks to months for insights | Hours to days for insights |
| Accuracy | Limited by human capacity/pre-set rules | Higher, data-driven, adaptive |
| Cost | High due to manual effort | Reduced by automation and efficiency |
| Document Processing | Slow, manual, error-prone | 50% faster, improved quality |
| Study Oversight | Weeks for trial insights | 75% time savings, insights in hours |
| Data Review Cycles | Manual, lengthy | Up to 80% faster per review cycle |
| Subpopulation Analysis | Labor-intensive, hypothesis-driven | Efficient, multi-variate outlier insights |
| Anomaly Detection | Reactive, often delayed | Proactive, real-time |
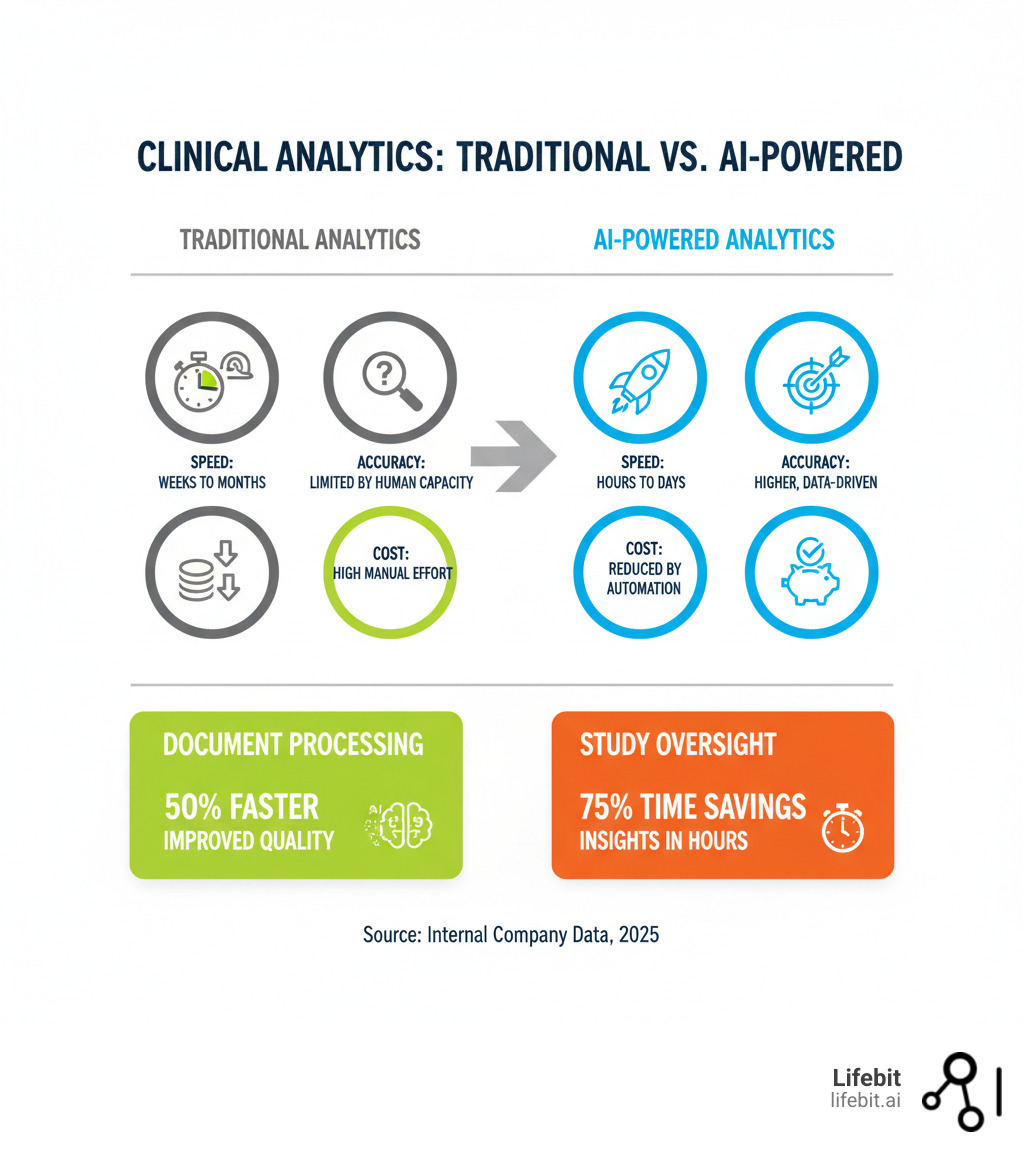
These numbers represent real operational change. When you get trial insights in hours instead of weeks (75% time savings) or run data review cycles 80% faster, you’re not just saving time. You’re catching issues earlier, keeping trials on track, and getting therapies to patients sooner. That’s the AI edge.
Break Down Data Barriers: The Top Challenges (And How to Beat Them)
Despite the promise of modern analytics and AI, clinical research data analytics still faces serious roadblocks. The main culprits are data quality, integration, privacy, and scalability. But for every barrier, there is a proven strategy to overcome it, guided by strong Clinical Data Governance.

Challenge 1: End Data Silos and Harmonize for Real Results
Data silos are the number one enemy of effective analytics. When patient information, genomic data, and trial results are trapped in separate systems that don’t speak the same language, you’re making critical decisions with only partial information.
The solution is to flip the script: spend 80% of your time analyzing data, not wrestling with it. This requires modern data integration platforms and data harmonization—the process of converting different formats into a common standard. Using a Common Data Model (CDM) like OMOP is crucial for making this work at scale. Harmonization is not just a technical task; it requires deep domain expertise to ensure clinical meaning is preserved when mapping data from disparate sources. By implementing robust Clinical Data Integration Platforms, we can break down these silos and open up insights that were previously impossible to see. Our guide to Data Harmonization dives deeper into these solutions.
Challenge 2: Secure, Compliant Analytics with Federated Technology
Meaningful analysis requires comprehensive data, but that data is protected by strict regulations like GDPR and HIPAA. You can’t just move sensitive patient information around. This creates a tension between the need for insight and the need to protect privacy.
Federated technology solves this dilemma. Instead of bringing data to the analysis, it brings the analysis to the data. The process is elegant and secure: a central server sends an analysis query or machine learning model to each data location (e.g., a hospital’s secure server). The model is trained locally on the data within that secure environment. Only the aggregated, non-identifiable results or updated model parameters are sent back. The raw, sensitive information never leaves its secure home, yet you can run sophisticated analytics across multiple datasets.
Trusted Research Environments (TREs) create secure, controlled spaces where researchers can access sensitive data under strict governance. Learn more about what makes a Trusted Research Environment effective. At Lifebit, our federated AI platform takes this further, enabling secure, real-time access to global biomedical data without ever moving it. Our platform includes the Trusted Research Environment (TRE), Trusted Data Lakehouse (TDL), and R.E.A.L. (Real-time Evidence & Analytics Layer) to deliver real-time insights and secure collaboration. This approach provides the comprehensive analysis you need while maintaining strict compliance with Data Security in Research protocols. Our work in Federated Data Analysis enables global collaboration that was impossible before.
Key Challenges in Clinical Research Data Analytics
Beyond silos and privacy, other critical challenges include:
- Data Quality and Completeness: Real-world data from sources like EHRs is often messy, incomplete, and not collected for research purposes. This “missingness” is rarely random and can introduce significant bias. Advanced analytics must incorporate methods for data cleaning, imputation, and sensitivity analyses to account for these imperfections.
- Integrating Multi-Omic Data: The complexity of integrating diverse data types—genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, etc.—is immense. Each ‘omic’ layer provides a different view of a patient’s biology, and combining them requires sophisticated bioinformatics skills and computational power to uncover meaningful biological signals.
- Informed Presence Bias: As noted in the known analytic challenges of EHR data, the data recorded is influenced by how often a patient interacts with the healthcare system. Overcoming this requires careful study design and statistical adjustment to avoid the risks of a “gold rush” mentality toward big data in health care.
Launch Your Career: How to Become a Clinical Data Analyst and Make an Impact
Are you fascinated by the intersection of healthcare and technology? A career in clinical research data analytics might be your calling. The demand for skilled analysts is rising globally, offering impactful career opportunities to be on the front lines of medical science.

Clinical data analysts are the heroes who translate raw data into the insights that drive breakthroughs.
The Role, Salary, and Where to Work
A Clinical Research Data Analyst (CRDA) bridges the gap between raw trial data and actionable insights. Key responsibilities include:
- Data Management: Overseeing data collection and storage to ensure accuracy and compliance.
- Trend Identification: Analyzing trial data to identify significant trends and correlations using statistical software like SAS or R.
- Reporting: Summarizing and presenting findings to researchers and other stakeholders.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring all processes comply with standards like GCP and HIPAA.
The median annual salary for clinical data analysts is approximately $72,590 as of August 2023, according to Payscale, with significant variation based on experience, education, and location. Analysts are in high demand at pharmaceutical companies, contract research organizations (CROs), hospitals, and health-tech companies. For more details, you can learn More on the Clinical Data Analyst role.
Must-Have Skills and Certifications
To excel in this role, you need a blend of analytical, clinical, and technical skills.
Essential Skills:
- Analytical & Statistical Skills: The ability to interpret complex data and use statistical software (SAS, R, SPSS).
- Clinical Knowledge: An understanding of trial protocols, medical terminology, and disease states.
- Communication & Attention to Detail: The ability to articulate findings clearly and handle sensitive data with precision.
Educational Pathways & Certifications:
A bachelor’s degree in a quantitative field (data analytics, statistics) or a life science is a common starting point. Advanced degrees in health informatics or data analytics can significantly boost career prospects.
While not always required, certifications validate your expertise. Consider pursuing credentials in areas like:
- Health data analysis
- Clinical data management
- SAS programming for clinical trials
- Good Clinical Practice (GCP)
For a comprehensive guide, refer to How to Become a Clinical Data Analyst. These skills will equip you to make a significant impact in the evolving world of clinical research.
Clinical Research Data Analytics: Your Top Questions Answered
We know navigating clinical research data analytics can be complex. Here are straight answers to the most common questions we hear.
What’s the #1 Goal of Clinical Research Data Analytics?
The single most important goal is to transform raw clinical trial data into reliable evidence that saves lives. It’s about assessing the safety and efficacy of new treatments and accelerating their path to the patients who need them. We’re not just crunching numbers; we’re turning them into knowledge that can change a life.
How Is AI Different from Traditional Analysis in Clinical Trials?
Traditional analysis tests a specific, pre-defined hypothesis. It’s structured and rigorous.
AI, particularly machine learning, is different. It learns from vast amounts of data to find complex patterns and relationships that humans would miss. It doesn’t just answer the questions we think to ask—it uncovers insights we didn’t even know to look for. AI amplifies traditional analysis, leading to faster findies and smarter predictions.
What’s the Biggest Challenge in Clinical Data Analytics Today?
The biggest challenge is securely accessing and integrating large, diverse, and siloed datasets while complying with strict privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
Clinical, genomic, and real-world data are scattered across different institutions in different formats. Bringing it all together for analysis is a massive technical and regulatory hurdle. This data fragmentation is the single biggest factor holding back progress.
That’s why federated technology and platforms like Trusted Research Environments are so critical. They allow us to analyze data where it lives, breaking down silos without compromising patient privacy. It’s the key to open uping global collaboration and accelerating breakthroughs, a challenge Federated Data Analysis is built to solve.
The Future Is Federated: Connect Global Data, Cure Faster—Don’t Get Left Behind
The future of clinical research data analytics isn’t just more data or better algorithms. It’s about connecting global data responsibly and efficiently. The next frontier is federated learning and real-time evidence, and it’s already here.
What if researchers could analyze diverse datasets from across continents without ever moving sensitive patient data? No massive data transfers, no regulatory nightmares, and no compromised privacy. This is the reality of federated technology.
Instead of moving data to a central location, the analysis comes to the data. Algorithms travel to secure environments, analyze information locally, and share back only aggregated, non-identifiable insights. The raw data never moves. This enables:
- Global collaboration that respects privacy laws like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Accelerated findies by pooling insights from millions of patients without pooling their records.
- Real-time evidence generation for adaptive trials and faster decisions.
- Unbreakable data security by keeping raw data where it belongs.
Federated technology solves the biggest barriers in clinical research: trust, privacy, and integration. At Lifebit, our next-generation federated AI platform is built on this vision. It enables secure, real-time access to global biomedical data, powering large-scale research for biopharma and public health agencies. Our platform includes the Trusted Research Environment (TRE), Trusted Data Lakehouse (TDL), and R.E.A.L. (Real-time Evidence & Analytics Layer) to deliver insights in hours, not weeks.
The research landscape is moving fast. Organizations that adopt federated technology now will lead the next decade of medical innovation. Those that don’t risk being left behind. The future is federated. Find out how Lifebit’s Federated Biomedical Data Platform can transform your research and help you cure faster.

